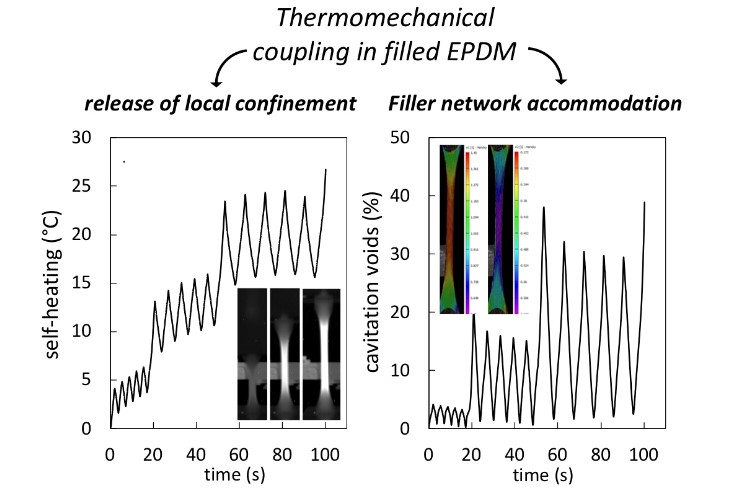
The effect of the strain rate on damage in carbon black filled EPDM stretched during single and multiple uniaxial loading is investigated. This has been performed by analysing the stress-strain response, the evolution of damage by Digital Image Correlation (DIC), the associated dissipative heat source by InfraRed thermography (IR), and the chains network damage by swelling. The strain rates were selected to cover the transition from quasi-static to medium strain rate conditions. In single loading conditions, the increase of the strain rate yields in a preferential damage of the filler network while rubber network is preserved. Such damage is accompanied by a stress softening and an adiabatic heat source rise. Conversely, increasing the strain rate in cyclic loading conditions yields in a filler network accommodation and a high self-heating whose combined effect is proposed as a possible cause of the ability of filled EPDM to limit damage, by reducing cavities opening during loading and favoring cavities closing upon unloading.