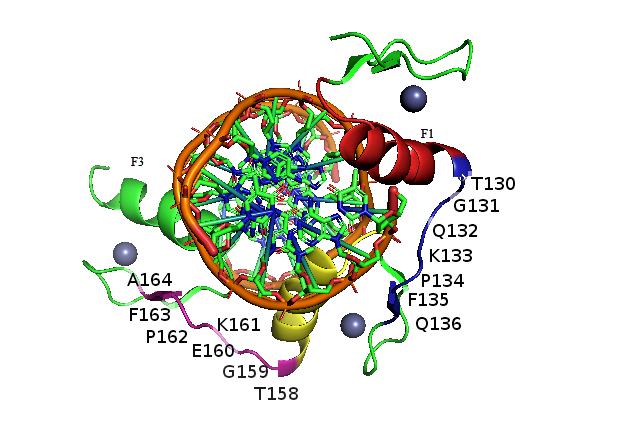
Zinc finger proteins (ZFP) play important roles in cellular processes. The DNA binding region of ZFP consists of 3 zinc finger DNA binding domains connected by amino acid linkers, the sequence TGQKP connects ZF1 and ZF2, and TGEKP connects ZF2 with ZF3. Linkers act to tune the zinc finger protein in the right position to bind its DNA target, the type of amino acid residues and length of linkers reflect on ZF1-ZF2-ZF3 interactions and contribute to the search and recognition process of ZF protein to its DNA target. Linker mutations and the affinity of the resulting mutants to specific and nonspecific DNA targets were studied by MD simulations and MM_GB(PB)SA. The affinity of mutants to DNA varied with type and position of amino acid residue. Mutation of K in TGQKP resulted in loss in affinity due to the loss of positive K interaction with phosphates, mutation of G showed loss in affinity to DNA, WT protein and all linker mutants showed loss in affinity to a nonspecific DNA target, this finding confirms previous reports which interpreted this loss in affinity as due to ZF1 having an anchoring role, and ZF3 playing an explorer role in the binding mechanism. The change in ZFP-DNA affinity with linker mutations is discussed in view of protein structure and role of linker residues in binding.