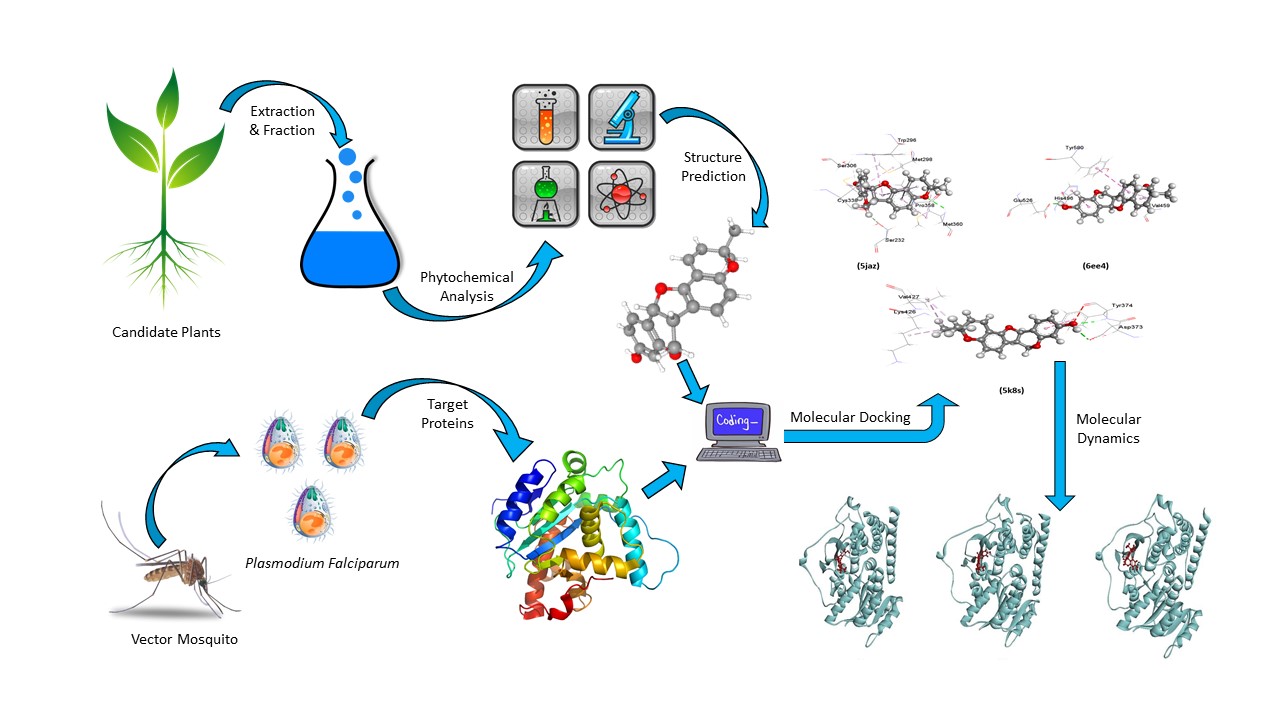
The exploration of alternative antimalarial therapeutics is a requisite for the emergence of resistance against Artemisinin. Considering the required cost and time length of classical small molecule drug discovery process, phytochemical screening of traditionally used medicinal plant which are repertoire of active compounds with antimalarial activity has become popular. To investigate the antimalarial property of traditionally used medicinal plants, a number of Erythrina spp have been reviewed systematically where less studied E. fusca has been selected for further analysis. Phytochemical investigation yielded five compounds namely; Phaseolin, Phytol, β-amyrin, Lupeol, and Stigmasterol. In-vitro antimalarial drug sensitivity HRP-II ELISA was carried out against chloroquine (CQ) sensitive 3D7 and CQ-resistant Dd2 strains. Extracts showed significant antimalarial activity against 3D7 and Dd2 strains (IC50 4.94 – 22 µg/mL) and these compounds have been reported here for the first time. Molecular docking analysis showed high binding energy (−9.0 ± 0.32 kcal/mole) indicating high degree of interaction between Phaseolin and 14 clinically important Plasmodium falciparum proteins at the active site. Stable interaction was also observed between ligand and protein from molecular dynamics simulation analysis with high free energy (−75.156 ± 11.459) that substantiates the potential of Phaseolin as an antimalarial drug candidate.