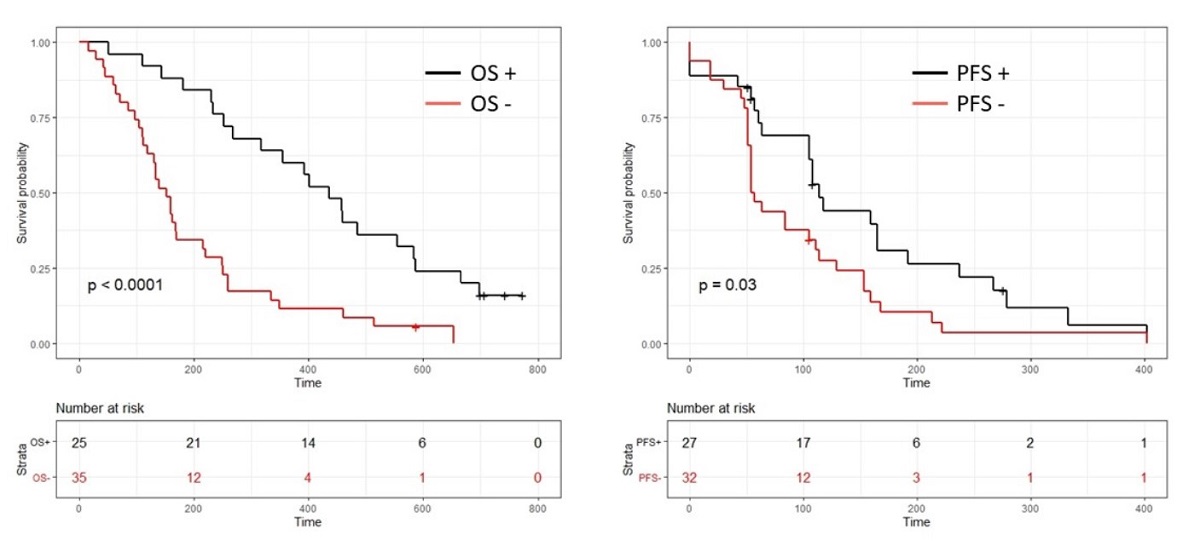
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is expected to be the second cause of cancer death by 2022. For nearly 80% of patients, diagnosis occurs at an advanced, non-surgical stage, making such patients incurable. Gemcitabine is still an important component in PDAC treatment and is most often used as a backbone to test new targeted therapies and there is, to date, no routine biomarker to predict its efficacy. Samples from a phase III randomized trial were used to develop trough a large approach based on blood-based liquid biopsy, transcriptome profiling, and machine learning, a 9 gene predictive signature for gemcitabine sensitivity. Patients with a positive test (41.6%) had a significantly longer progression free survival (PFS) (3.8 months vs. 1.9 months p=0.03) and a longer overall survival (OS) (14.5 months vs. 5.1 p<0.0001). In multivariate analyses, this signature was independently associated with PFS (HR=0.5 (0.28-0.9) p=0.025) and OS (HR=0.39 (0.21-0.7) p=0.002).