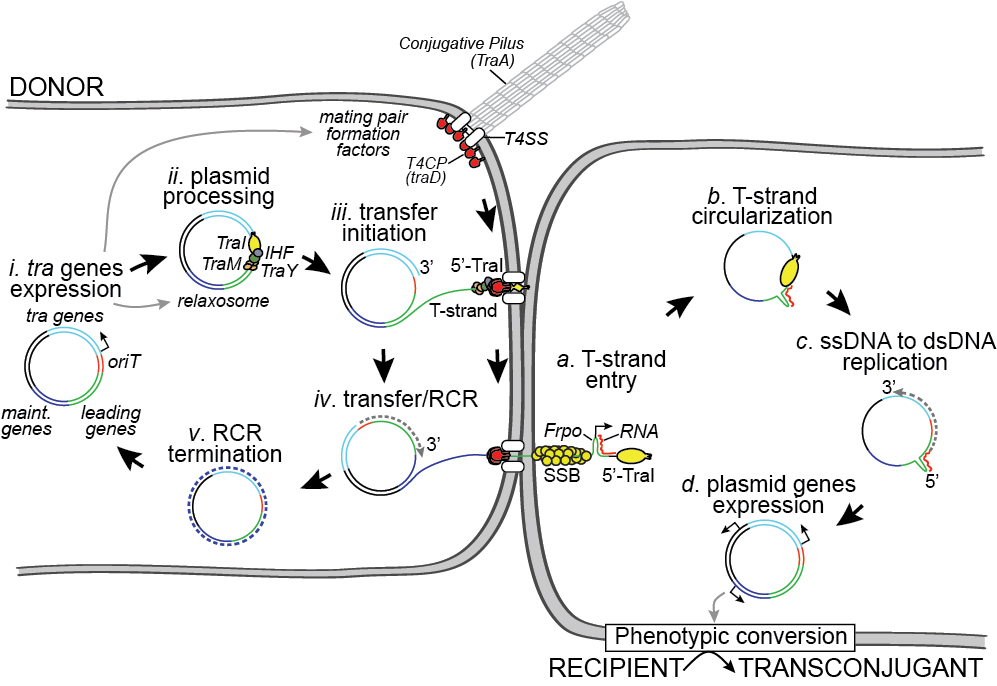
Bacterial conjugation, also referred to as bacterial sex, is a major horizontal gene transfer mechanism where the DNA is transferred from a donor to a recipient bacterium by direct contact. Conjugation is universally conserved among bacteria and occurs in a wide range of environments (soil, plant surfaces, water, sewage, biofilms and host-associated bacterial communities). Within these habitats, conjugation drives the rapid evolution and adaptation of bacterial strains by mediating the propagation of various metabolic properties, including symbiotic life-style, virulence, biofilm formation, or resistance to heavy metals and, most importantly, resistance to antibiotics. These properties make of conjugation a fundamentally important process at the center of extensive study. Here, we review the key steps of conjugation by following the life-cycle of the F plasmid during transfer from the donor to the recipient cell. We also discuss our current knowledge of the extent and impact of conjugation within an environmentally and clinically relevant bacterial habitat, bacterial biofilms.