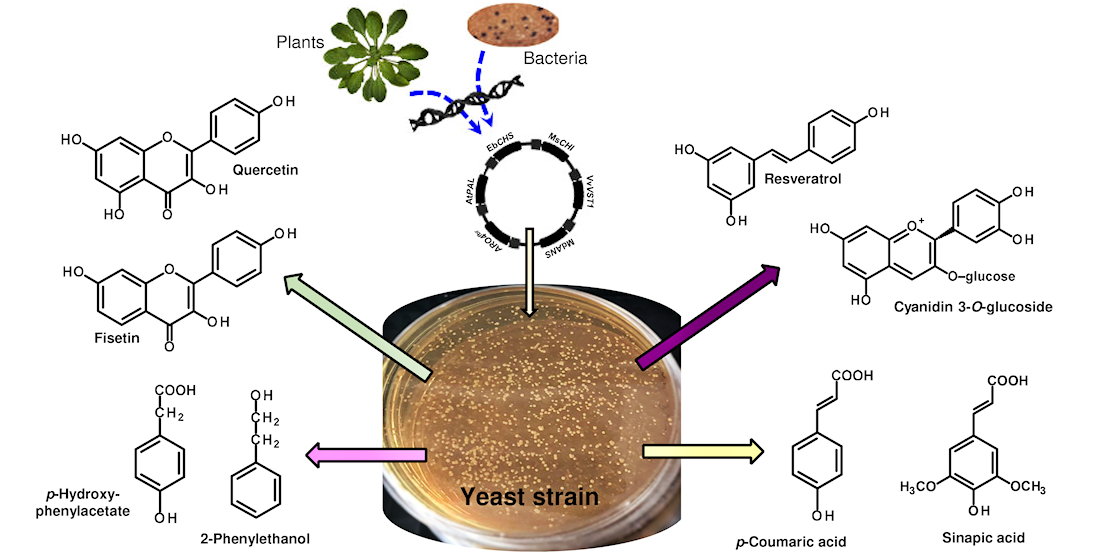
Secondary phenolic metabolites are defined as valuable natural products synthesized by different organisms that are not essential for growth and development. These compounds play an essential role in plant defense mechanisms, and an important role in the pharmaceutical, cosmetics, food, and agricultural industries. Despite the vast chemical diversity of natural compounds, their content in plants is very low, in consequence, it eliminates the possibility of the production of these interesting secondary metabolites from plants. Therefore, microorganisms are widely used as cell factories by industrial biotechnology to the production of different non-native compounds. Among microorganisms commonly used in biotechnological applications, yeasts are prominent host for the diverse secondary metabolite biosynthetic pathways. Saccharomyces cerevisiae is often regarded as the better host organism for the heterologous production of phenolics compounds, especially if the expression of different plant genes is necessary.