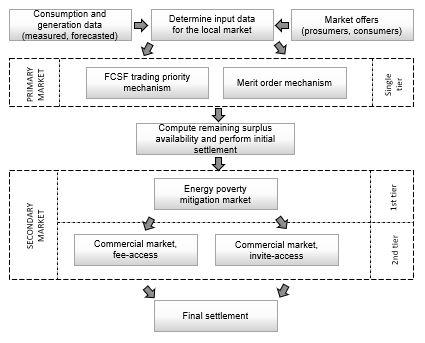
The deregulated markets have replaced the traditional way of trading electricity from the producers to the consumer, via government-owned organizations and regulated tariffs. Nowadays, electricity prices are determined by the offer-demand mechanism and consumers can negotiate tariffs with their supplier of choice. For classic wholesale suppliers, the tariffs are a result of the transactions performed on the wholesale market and the energy mix available in certain geographical regions. In parallel with becoming eligible and participating in retail electricity markets, the consumers use increasingly local generation sources based mostly on renewable energy technologies such as PV panels, and become prosumers. They want to be able to sell back to the market the generation surplus, in order to obtain the maximum benefits from their initial investment. Currently, several trading mechanisms for prosumers are available, ranging from the simplest, selling back the surplus to an aggregator at fixed tariffs, to more complex market schemes. This paper proposed a two-tier local market model for prosumers and consumers connected in microgrids, based on the blockchain technologies and other technologies and concepts such as remote sensing, smart grids, crowdsourcing and energy poverty.