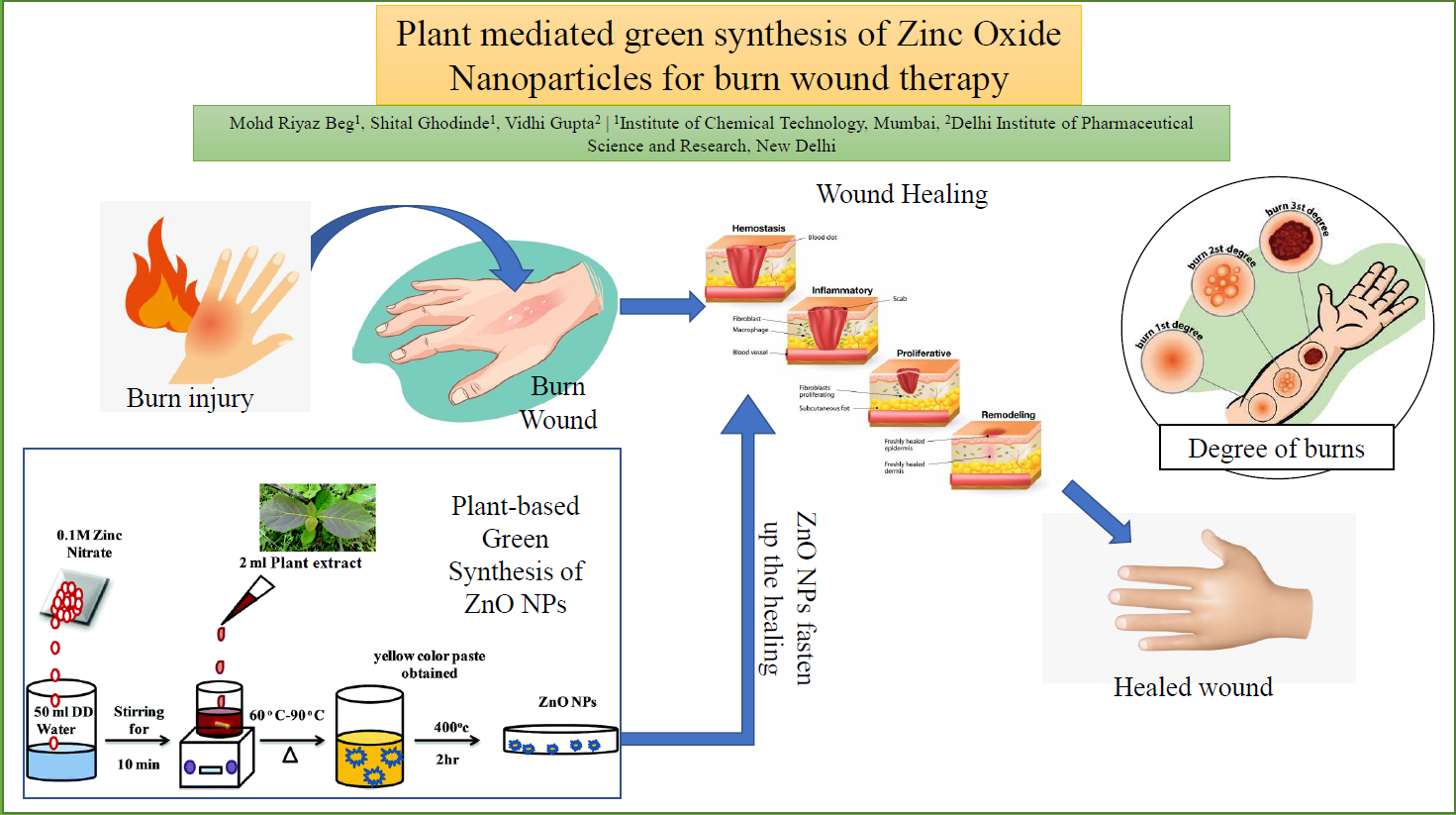
In this changing world, we all are surrounded by the surmountable risk of getting injured. Amongst various risk factors, major burns are the most distressing and catastrophic. Burn wounds are not easy to heal via natural healing process and ultimately ended up with scar formation. If the degree of burn is high then the loss of tissue and its function is very common. To fasten-up the natural burn wound healing; zinc, an essential trace element is found to be very much effective. But due to its’ particle size limitation, less contact with wounded cells and tissues, and high inherent toxicity restrict its use. Needlessly, zinc is an element with dual action i.e. both antimicrobial and wound healing it is a prime choice to apply its aptitude in burn wound healing. To overcome the documented limitations zinc has converted to nanoparticle form. Zinc oxide nanoparticles, in particular, have attained ample of interest due to their unique properties and potential antimicrobial activity along with wound healing activity which makes it promising for the healing of topical burn wounds. Plant mediated green synthesis of nano-metal oxide particles is gaining a lot of significance due to its simplicity, eco-friendliness and extensive antimicrobial activity and recommended as an appealing substitute to not only physical methods but also chemical methods avoiding the use of the high rate of toxic chemicals and extreme surroundings. This study includes ZnO NPs role in burn wound healing with Phyto-mediated synthesis methods to provide evidence of their potential applications. Additionally, it provides an overview of traditional methods used for the synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and characterization techniques to obtain information concerning the size, shape and optical properties along with toxicity and safety concern of ZnO NPs and its biomedical applications.