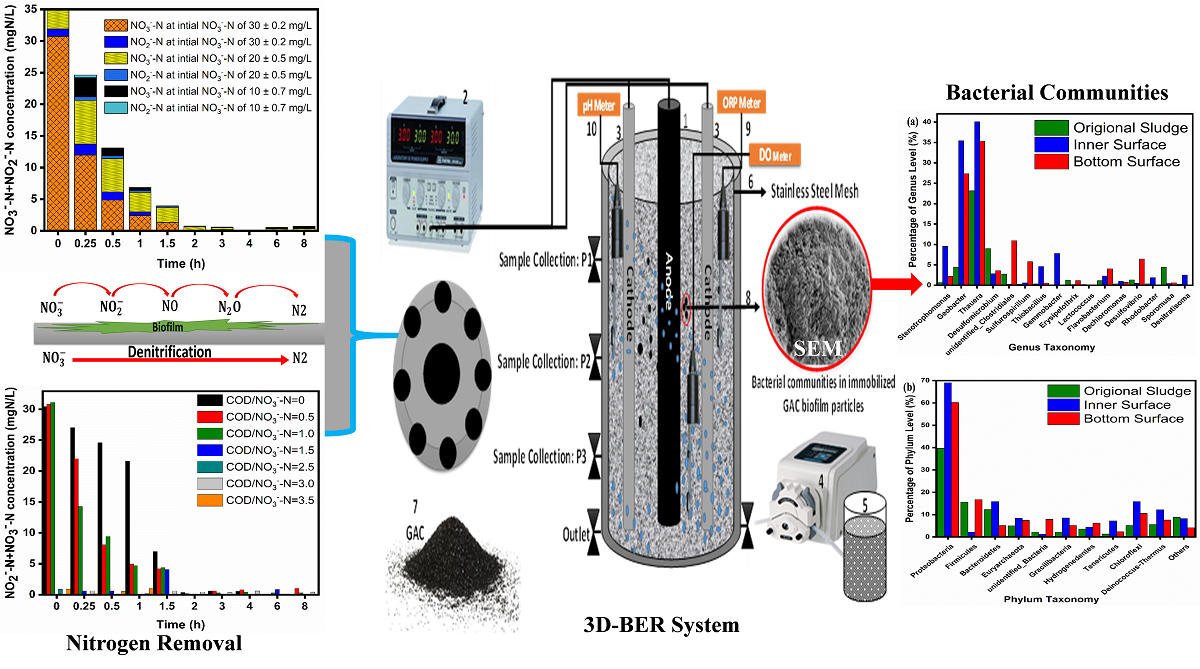
In this study, a three-dimensional bioelectrochemical reactor system (3D-BERs) with granular activated carbon (GAC) epitomizes a novel treatment technology for treating nitrate-polluted water. The conventional denitrification process faces many challenges, including the huge demand for organic carbon, long-term accumulation of intermediate products, and the adaptation period. Results shown that under the optimal conditions of the COD/NO3--N ratio was 1.5, the denitrification efficiency reached 98.62%, when compared to 81.12% at COD/ NO3--N ratio of 3.5, and the initial pH of 7.5 ± 0.5, NO3--N was entirely removed at 2.2 h without accumulation of nitrite. The high initial ratio of NO2--N/NO3--N is mainly to accelerate the denitrification rate by accelerating the reduction of nitrite. Denitrification process followed by zero-order kinetics linear model for at different concentrations of inlet NO3--N, and achieved higher denitrification rate at greater inlet NO3--N concentration. High-throughput sequencing shows that the community structure and relative abundance of bacteria changed significantly, especially at the genes and the phyla level in immobilized GAC particles. Microbial composition enhanced the removal of nitrogen at the inner surface (IS) and bottom surface (BS) of immobilized GAC carriers. Therefore, this system is expected to be a more efficient and useful supplement or a cost-effective alternative compared to the traditional low carbon to nitrogen wastewater treatment system.