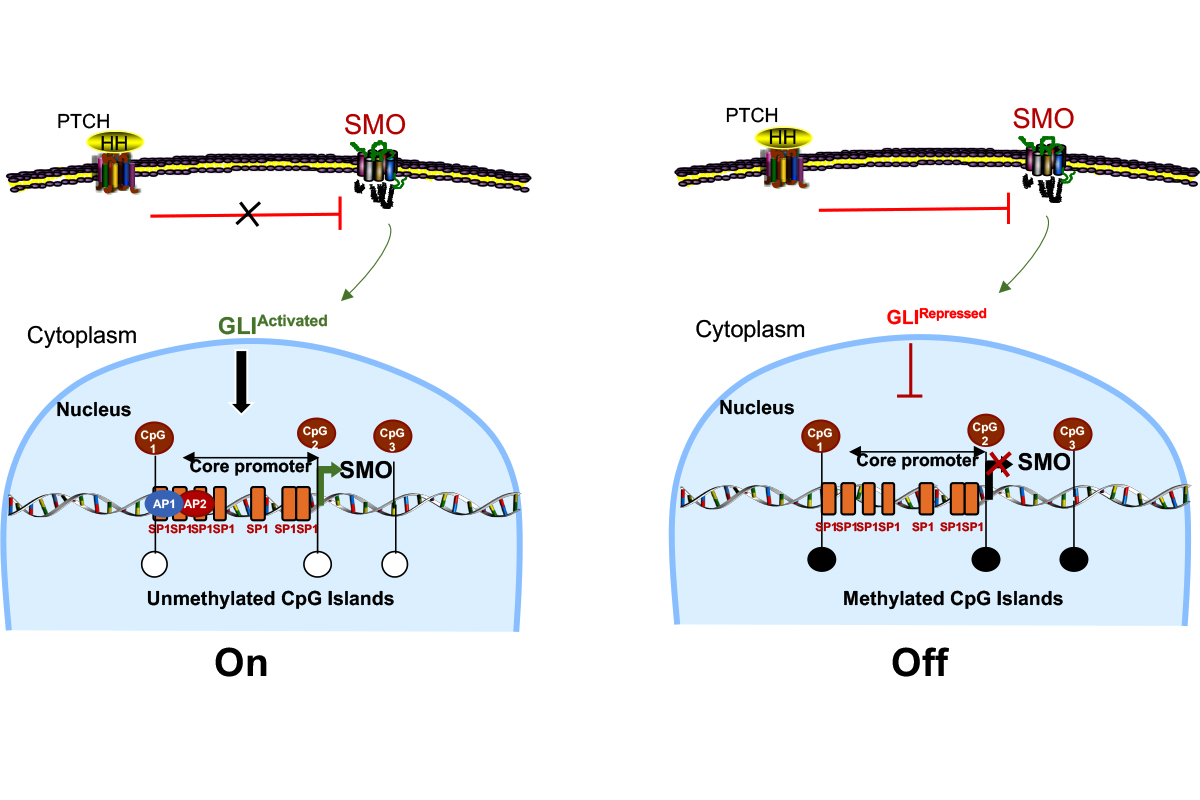
Background: The hedgehog (HH) signaling pathway is a key regulator of embryonic patterning, tissue regeneration, stem cell renewal, and cancer growth. The smoothened (SMO) protein regulates the HH signaling pathway and has demonstrated oncogenic activity. Methods: To clarify the role of the HH signaling pathway in tumorigenesis, the expression profile of key HH signaling molecules, including SMO, PTCH1, GLI1, GLI2, and GLI3, were determined in thirty-three cancer cell lines. We performed a computational analysis of the upstream region of the SMO gene to identify the regulatory elements. Results: Three potential CpG islands and several putative SMO promoter elements were identified. Luciferase reporter assays mapped key SMO promoter elements, and functional binding sites for SP1, AP1, CREB, and AP-2a transcription factors in the core SMO promoter region were confirmed. A hypermethylated SMO promoter was identified in several cancer cell lines suggesting an important role for epigenetic silencing of SMO expression in certain cancer cells. Discussion: These results have important implications for our understanding of regulatory mechanisms controlling HH pathway activity and the molecular basis of SMO gene function. Moreover, this study may prove valuable for future research aimed at producing therapeutic downregulation of SMO expression in cancer cells.