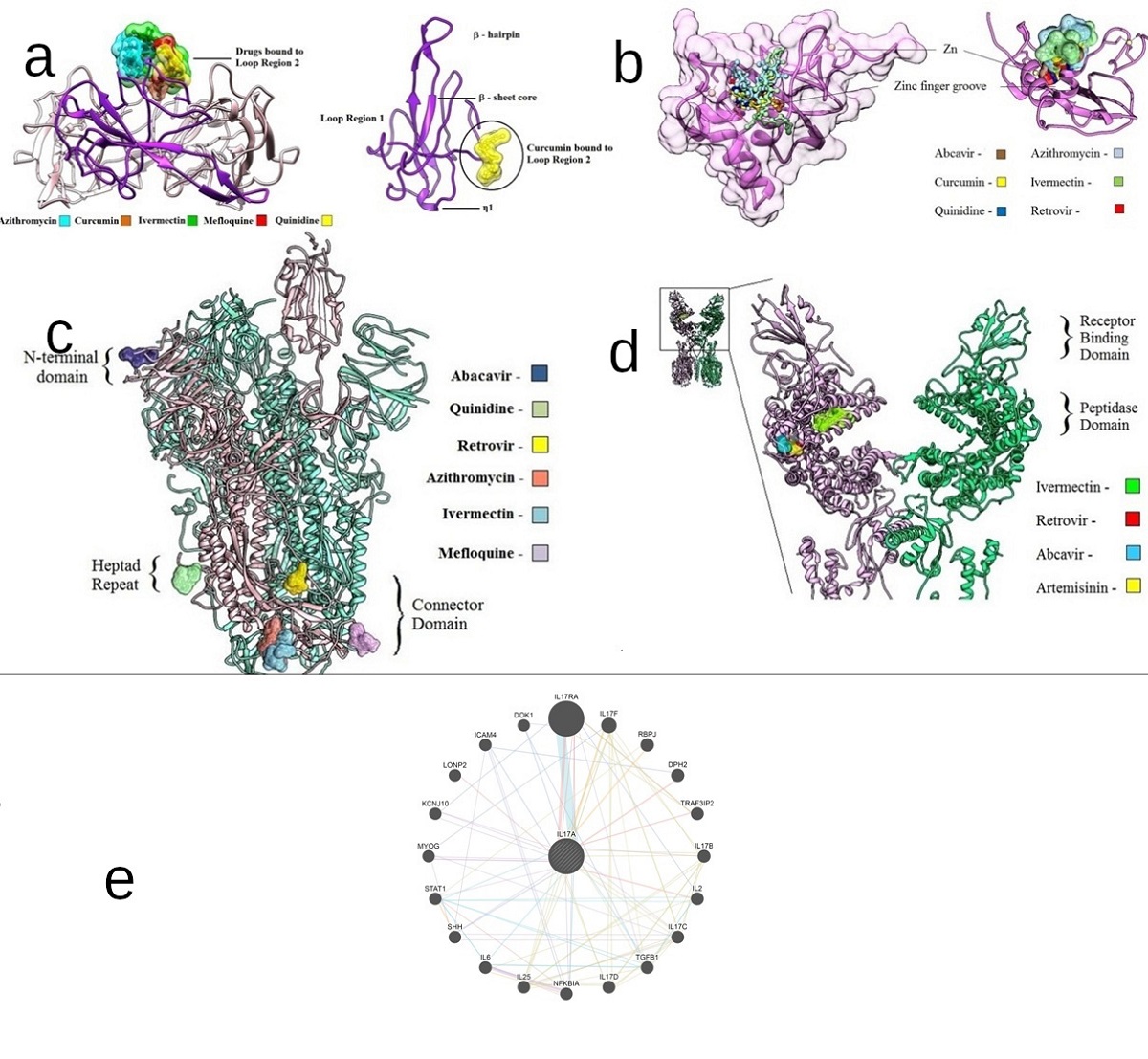
Corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is caused by a Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which is a positive strand RNA virus. The SARS-CoV-2 genome and its association to SAR-CoV-1 vary from ca. 66% to 96% depending on the type of betacoronavirdeae family members. With several drugs, viz. chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, ivermectin, artemisinin, remdesivir, azithromycin considered for clinical trials, there has been an inherent need to find distinctive antiviral mechanisms of these drugs. Curcumin, a natural bioactive molecule has been shown to have a therapeutic potential for various diseases, but its effect on COVID-19 has not been explored. In this study, we show the binding potential of curcumin targeted to a variety of SARS-CoV-2 proteins, viz. spike glycoproteins (PDB ID: 6VYB), nucleocapsid phosphoprotein (PDB ID: 6VYO), membrane glycoprotein (PDB ID: 6M17) along with nsp10 (PDB ID: 6W4H) and RNA dependent RNA polymerase (PDB ID: 6M71) structures. Our results indicate that curcumin has high binding affinity towards nucleocapsid and nsp 10 proteins with potential antiviral activity.