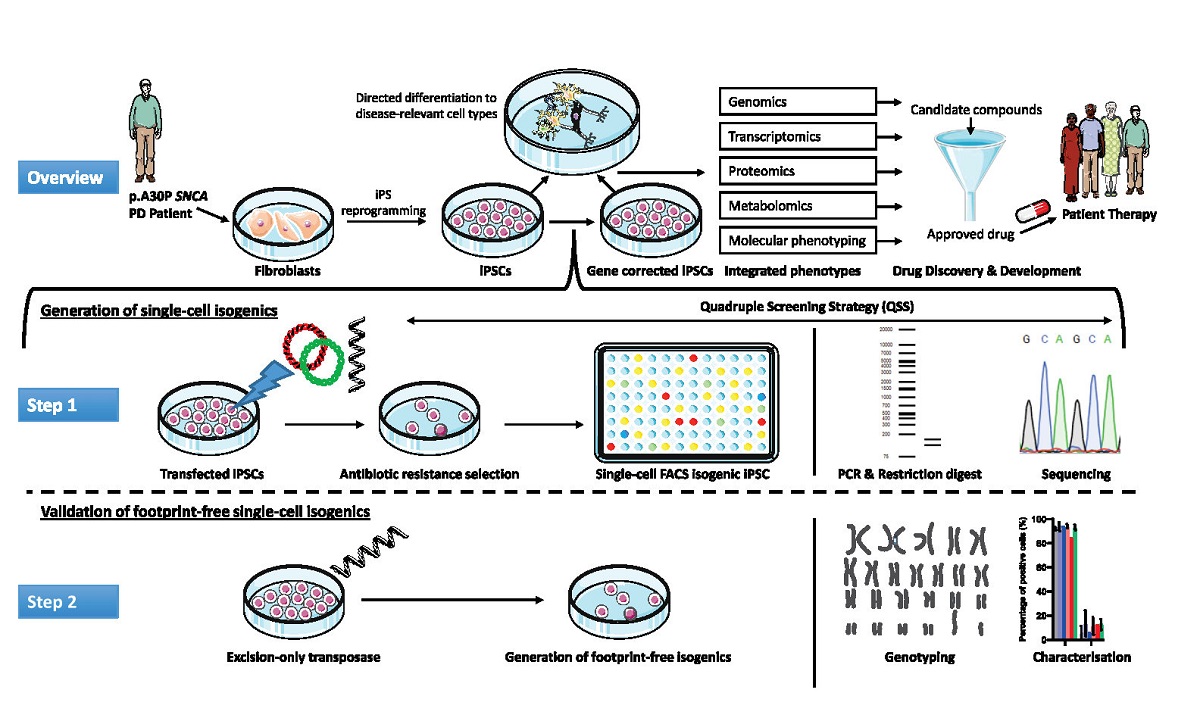
The generation of isogenic induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) lines using CRISPR-Cas9 technology is a technically challenging, time-consuming process with variable efficiency. Here we use fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) to sort biallelic CRISPR-Cas9 edited single-cell iPS clones into high-throughput 96-well microtiter plates. We used high-content screening (HCS) technology and generated an in-house developed algorithm to select the correctly edited isogenic clones for continued expansion and validation. In our model we have gene-corrected the iPSCs of a Parkinson’s disease (PD) patient carrying the autosomal dominantly inherited heterozygous c.88G>C mutation in the SNCA gene, which leads to the pathogenic p.A30P form of the alpha-synuclein protein. Undertaking a PCR restriction-digest mediated clonal selection strategy prior to sequencing, we were able to post-sort validate each isogenic clone using a quadruple screening strategy. Subsequent transfection with mRNA encoding excision-only transposase allows for the generation of footprint-free isogenic iPSC lines. These monoclonal isogenic iPSC lines retain a normal molecular genotype, express pluripotency markers and have the ability to differentiate into the three germ layers. This combinatory approach of FACS, HCS and post-sorted restriction digestion facilitates the generation of isogenic cell lines for disease modelling to be scaled-up on an automated platform.