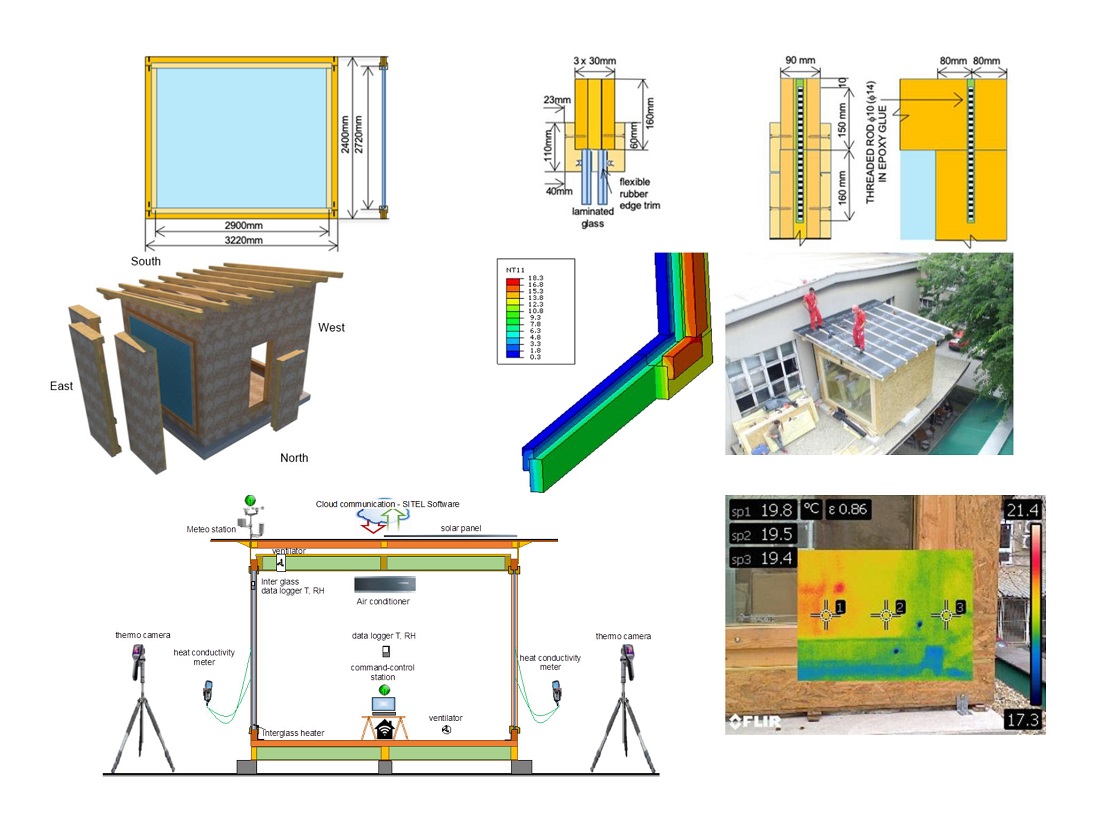
Facade elements are known to represent a building component with multiple performance parameters to satisfy. Among others, “advanced facades” take advantage of hybrid solutions, like the assemblage of laminated materials. In addition to enhanced mechanical properties that are typical of optimally composed hybrid structural components, these systems are energy-efficient, durable, and offer lightening comfort and optimal thermal performance. This is the case of the structural solution developed in joint research efforts of the University of Zagreb and the University of Ljubljana, within the Croatian Science Foundation VETROLIGNUM project. The design concept involves the mechanical interaction of timber and glass load-bearing members, without sealing or bonded glass-to-timber surfaces. Laminated glass infilled timber frames are recognized as a new generation of structural members with relevant load-carrying capacity (and especially the enhancement of earthquake resistance of framed systems), but also energy-efficient and cost-effective solutions.