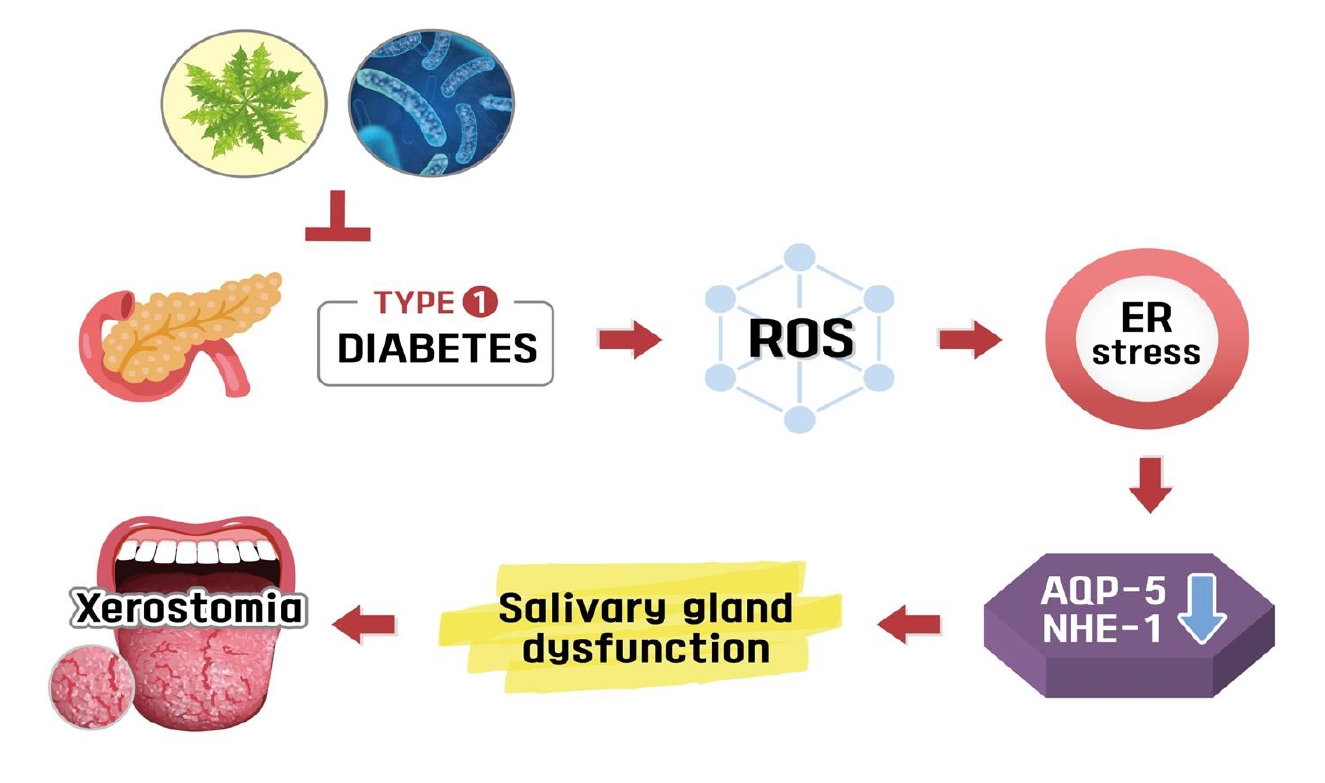
Dry mouth, hyposalivation, or xerostomia is a significant problem in diabetic patients; however, there was no way to relieve these symptoms. This study was aimed to evaluate the effects of Ixeris dentata (IXD) in combination with lactobacillus extract on the salivation rate in diabetes-induced dry mouth, and its mechanism was also investigated. In the streptozotocin-induced diabetes model, dry mouth condition was established as a model. Both control and diabetic rats were treated with a sublingual spray of either water or IXD and subsequently treated with or without a spray of lactobacillus extract. In diabetes condition, the salivary flow rate, amylase activity, and aquaporin-5 and Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE-1) expressions were markedly decreased, whereas they were more significantly recovered in the sequential treatment of IXD-lactobacillus extract than each single treatment. Furthermore, oxidative stress and its related ER stress response were especially regulated in the IXD/lactobacillus extract condition, where the following anti-oxidative enzymes; GSH:GSSG ratio, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) were involved. This study suggests that the combination of IXD and lactobacillus would be a potential alternative medicine against diabetes-induced hyposalivation and xerostomia.