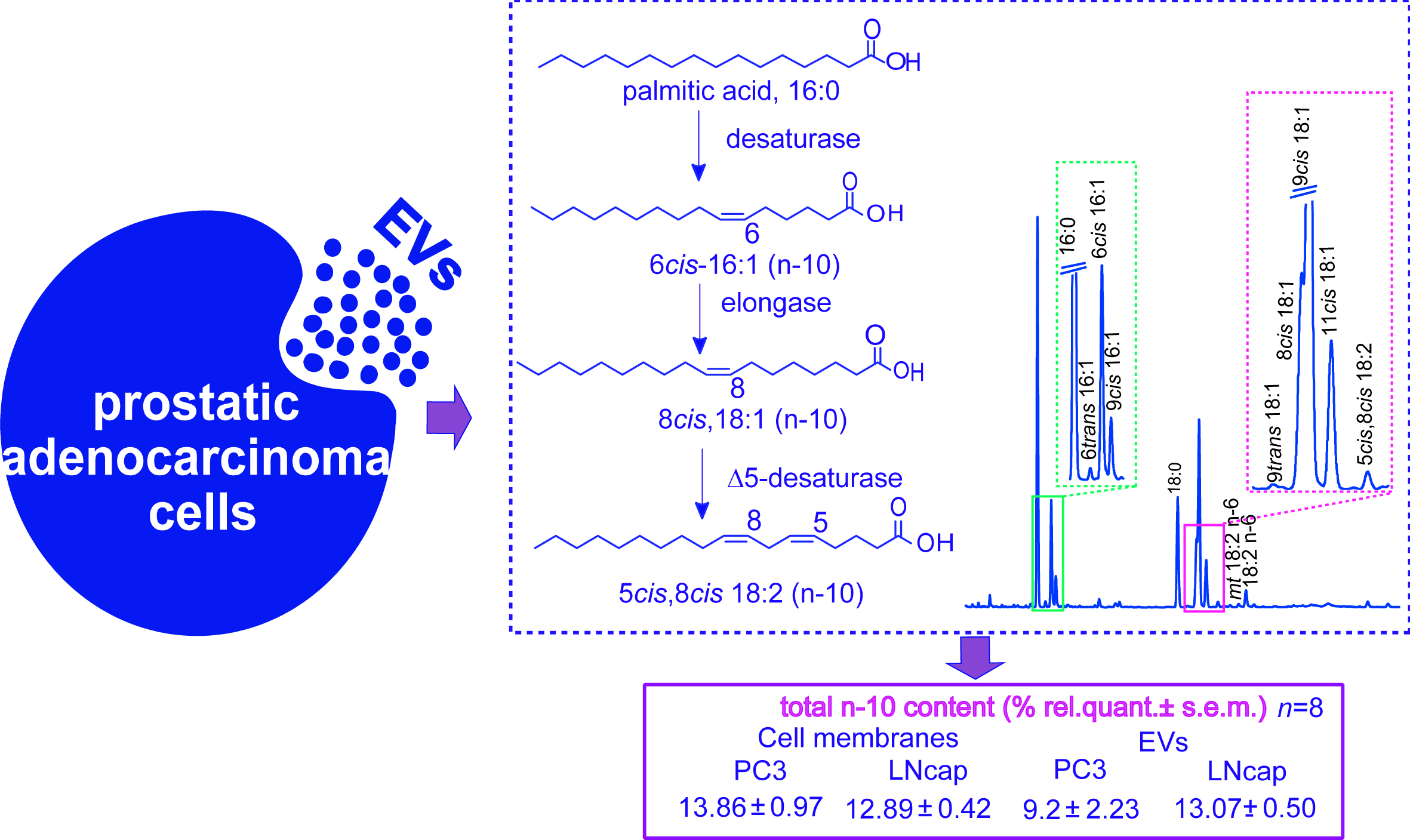
A new pathway leading to the n-10 fatty acid series has been recently evidenced, starting from sapienic acid - a monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) resulting from the transformation of palmitic acid by delta-6 desaturase. Sapienic acid attracts attention as novel marker of cancer cell plasticity. Here, we analyzed fatty acids including the n-10 fatty acid contents, and compared for the first time cell membranes and the corresponding extracellular vesicles (EV) of two human prostatic adenocarcinoma cell lines of different aggressiveness (PC3 and LNCaP). The n-10 components were 9-13% of the total fatty acids in both cancer cell lines and EVs, with total MUFA levels significantly higher in EVs of the most aggressive cell type (PC3). High sapienic/palmitoleic ratios indicated the preference for delta-6 vs. delta-9 desaturase enzymatic activity in these cell lines. The expressions analysis of enzymes involved in desaturation and elongation by qRT-PCR showed a higher desaturase activity in PC3 and a higher elongase activity toward polyunsaturated fatty acids than toward saturated fatty acids, compared to LNCaP cells. Our results improve the present knowledge in cancer fatty acid metabolism and lipid phenotypes, highlighting EV lipidomics to monitor positional fatty acid isomer profiles and MUFA levels in cancer.