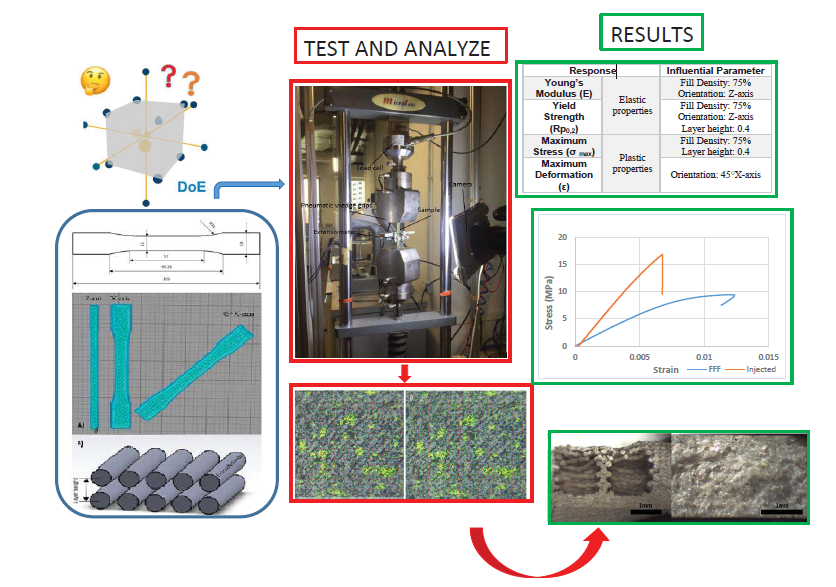
The present study evaluates the manufacturing parameters effects on the tensile properties of material composed by polylactic acid (PLA) with wood fibers known as Timberfill. The specimens were built through fused filament fabrication (FFF). The influence of four printing parameters (Layer height, Fill density, Printing velocity, and Orientation) are considered through a L27 Taguchi orthogonal array in order to reduce experimental runs. Tensile test is applied to obtain the response variable used as output results to perform the ANOVA calculations. Fill density is the most influential parameter on the tensile strength, followed by building orientation and layer height, whereas the printing velocity shows no significant influence. The optimal set of parameters and levels is found, being 75% fill density, 0○Z-axis orientation, 0.4 mm layer height, and 40 mm/s velocity as the best combination. Applying this combination showed 9.37 MPa in maximum tension. Lastly, five solid Timberfill specimens manufactured via injection molding technology were also tested and the results compared to the printed samples. The values of the elastic modulus, elastic limit, and maximum tension of the injected samples were almost twofold of those were obtained for the FFF samples, but the maximum elongation of injected specimens was fell sharply.