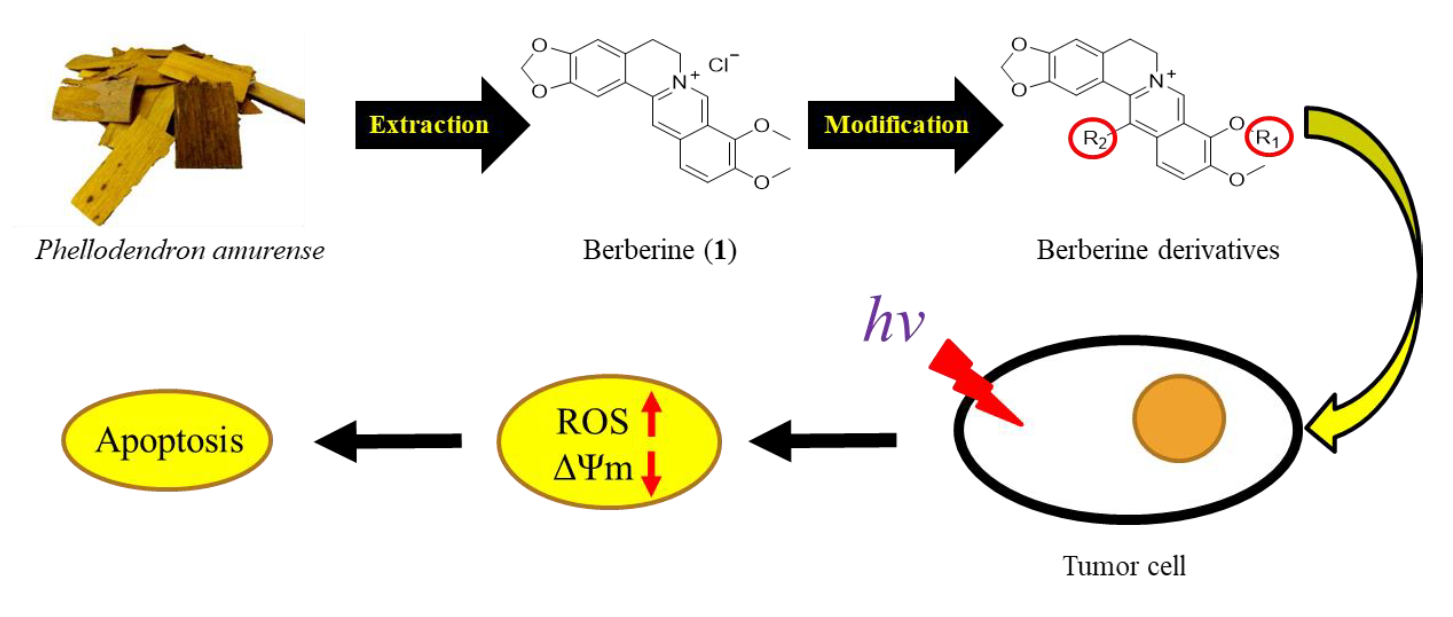
The objective of this study was to synthesize 9-/13-position substituted berberine derivatives and evaluated their cytotoxic and photocytotoxic effects against three human cancer cell lines. Among all the synthesized compounds, 9-O-dodecyl- (5e), 13-dodecyl- (6e) and 13-O-dodecyl-berberine (7e) exhibited stronger growth inhibition against three human cancer cell lines, (HepG2, HT-29 and BFTC905), in compare with structurally related berberine (1). These three compounds also showed the photocytotoxicity in human cancer cells in a concentration-dependent and light dose-dependent manner. Through flow cytometry analysis, we found out a lipophilic group at 9-/13-position of berberine may have facilitated its penetration into test cell and hence enhanced its photocytotoxicity on human liver cancer cell HepG2. Further, in cell cycle analysis, 5e, 6e and 7e induced HepG2 cells to arrest at S phase and caused apoptosis upon irradiation. In addition, photodynamic treatment of berberine (1) and its derivatives 5e, 6e and 7e again showed a significant photocytotoxic effects on HepG2 cells, induced remarkable cell apoptosis, greatly increased intracellular ROS level and the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential. These results over and again confirmed that berberine derivatives 5e, 6e and 7e greatly enhanced photocytotoxicity. Taking together, the test data led us to conclude that berberine derivatives with a dodecyl group at 9-/13-position could be great candidates for the anti-liver cancer medicines developments.