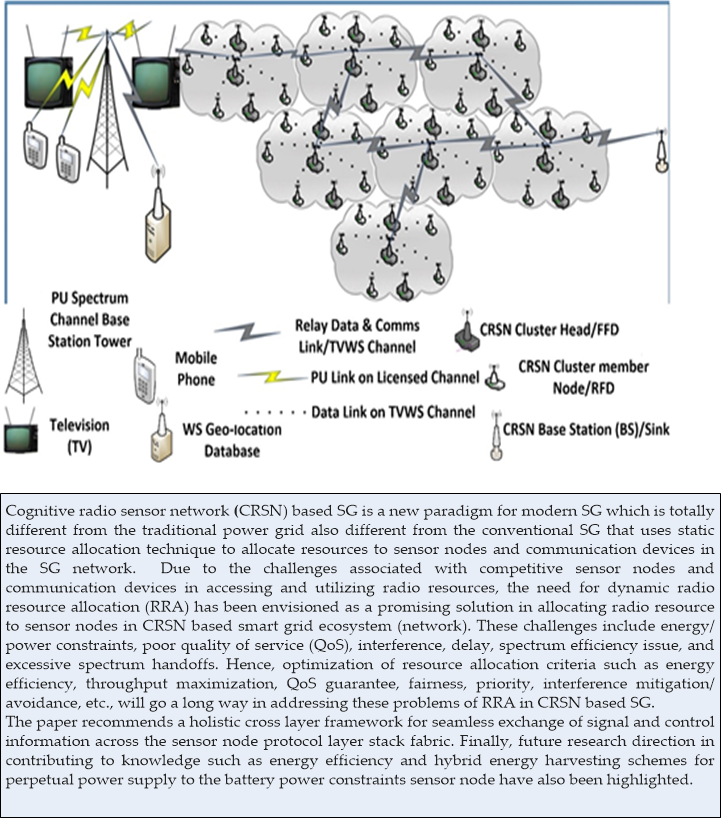
A cognitive radio sensor network (CRSN) based Smart Grid (SG) is a new paradigm for a modern SG. It is totally different from the traditional power grid and also different from the conventional SG that uses a static resource allocation technique to allocate resources to sensor nodes and communication devices in the SG network. Due to the challenges associated with competitive sensor nodes and communication devices in accessing and utilizing radio resources, the need for dynamic radio resource allocation (RRA) has been proposed as a solution for allocating radio resources to sensor nodes in a CRSN based smart grid ecosystem (network). These challenges include energy/power constraints, poor quality of service (QoS), interference, delay, spectrum efficiency issues, and excessive spectrum hand-offs. Hence, the optimization of resource allocation criteria, such as energy efficiency, throughput maximization, QoS guarantee, fairness, priority, interference mitigation/avoidance, etc., will go a long way in addressing the problems of RRA in a CRSN based SG. Consequently, this work explores RRA in CRSNs for SGs. Various resource allocation schemes, as well as its architecture in a CRSN for SG environment, are presented. The work reported in this paper introduces a model called the “guaranteed network connectivity channel allocation” for throughput maximization (GNC-TM) and optimal spectrum band determination in RRA for improved throughput criteria in CRSNs for SGs. The results show that the model outperforms the existing protocol in terms of throughput and error probability. Finally, the contribution to knowledge and future research direction, such as energy efficiency and hybrid energy harvesting schemes are highlighted.