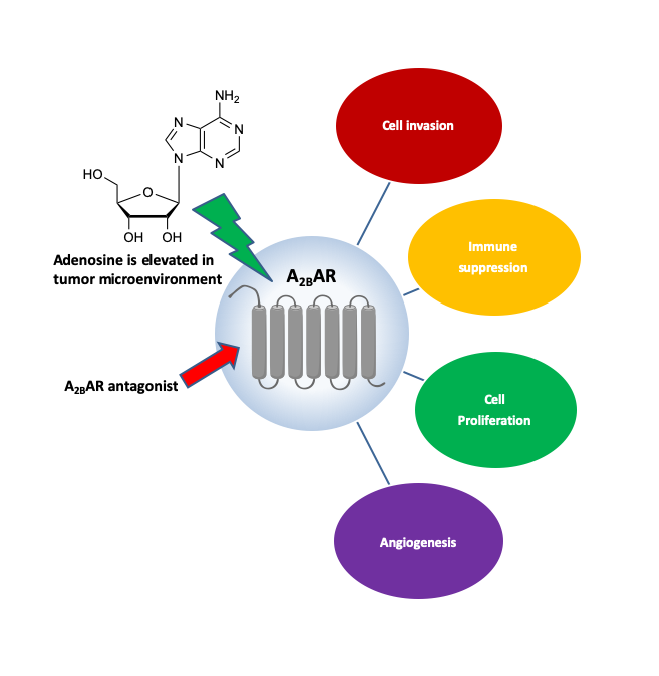
There are four subtypes of adenosine receptors (ARs), named A1, A2A, A2B and A3, all of which are G protein-coupled receptors. The A2BAR, coupled to both Gαi and Gαq G proteins, is one of the several G-protein-coupled receptors that are expressed in a significantly higher level in some cancer tissues in comparison to adjacent normal tissues. There is growing evidence that the A2BAR plays an important role in tumor cell proliferation, angiogenesis, metastasis, and immune suppression. Thus, A2BAR antagonists are potentially novel attractive anticancer agents. Several antagonists targeting at the A2BAR are currently in clinical trials for various types of cancers. In this review, we first describe the signaling, agonists, and antagonists of the A2BAR. We further discuss the role of the A2BAR in the progression of various types cancers, and the rationale of using A2BAR antagonists in cancer therapy