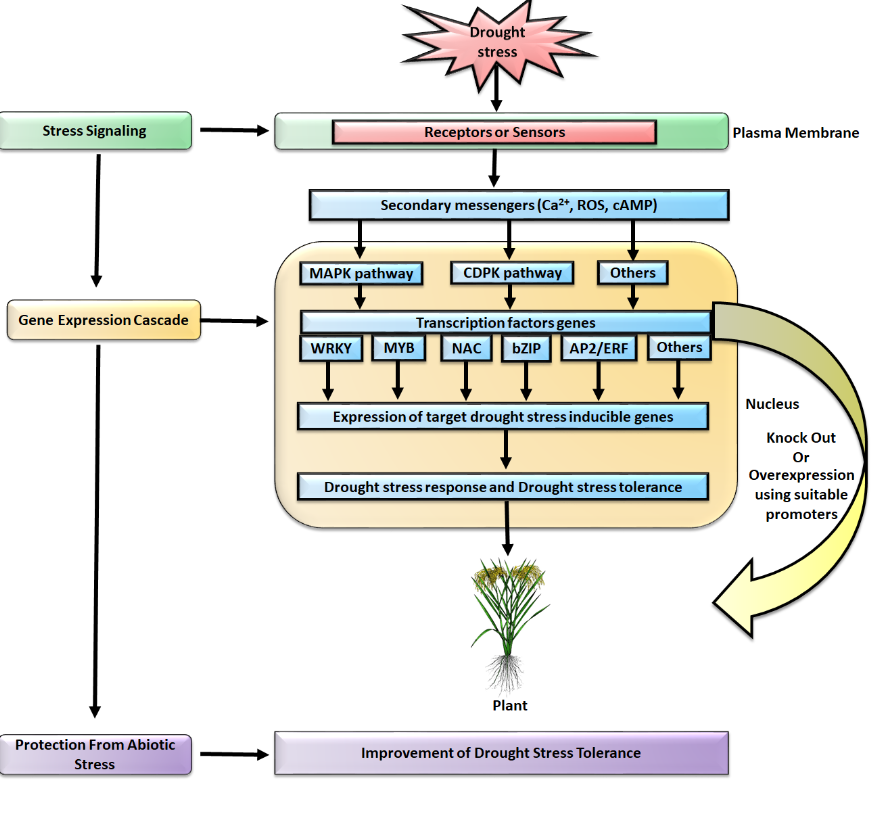
Many studies were done in the development of drought stress-tolerant transgenic plants, including crop plants. Rice is considered to be a vital crop target for improving drought stress tolerance. Much transgenic rice showed improved drought stress tolerance was reported to date. They are genetically engineered plants that are developed by using genes that encode proteins involved in drought stress regulatory networks. These proteins include protein kinases, transcription factors, enzymes related to osmoprotectant or plant hormone synthesis, receptor-like kinase. Of the drought stress-tolerant transgenic rice plants described in this review, most of them display retarded plant growth. In crop crops, plant health is a fundamental agronomic trait that can directly affect yield. By understanding the regulatory mechanisms of retarded plant growth under drought stress, conditions are necessary precursors to developing genetically modified plants that result in high yields.