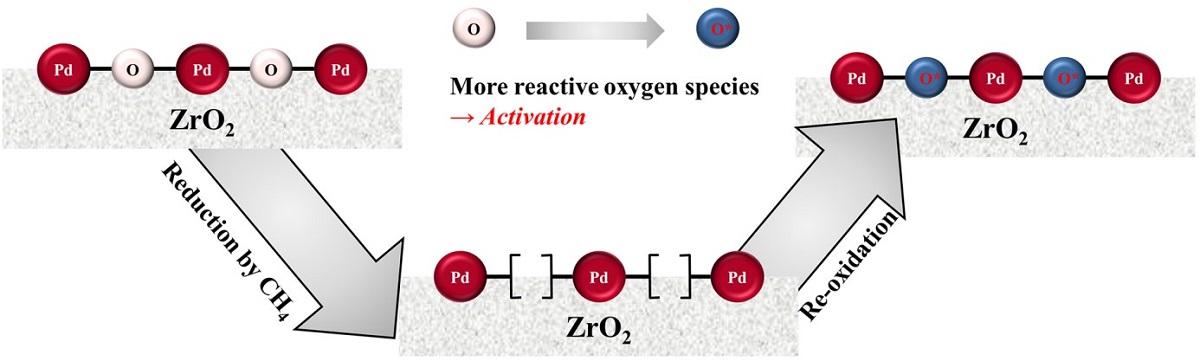
The improvement of the methane combustion activity was observed in cyclic temperature-programmed and isothermal reactions over Pd/ZrO2 catalysts by simple reduction/re-oxidation treatment. The catalytic activity increased during the initial stages of isothermal reaction, and the light-off temperature was lowered as the number of cycles increased in the cyclic temperature-programmed reaction. To reveal the origin of activation, variations in the reduction properties after the activation period were carefully investigated through CH4 temperature-programmed reduction (TPR) measurements. From the CH4-TPR results, it was confirmed that the reduction temperature decreased significantly after activation. The observation of the CH4-TPR peak at relatively low temperatures is directly proportional to the catalytic activity of CH4 combustion. It was therefore concluded that repeated reduction/re-oxidation occurred in the reactant stream, and this phenomenon allowed the combustion reaction to proceed more easily at lower temperatures.