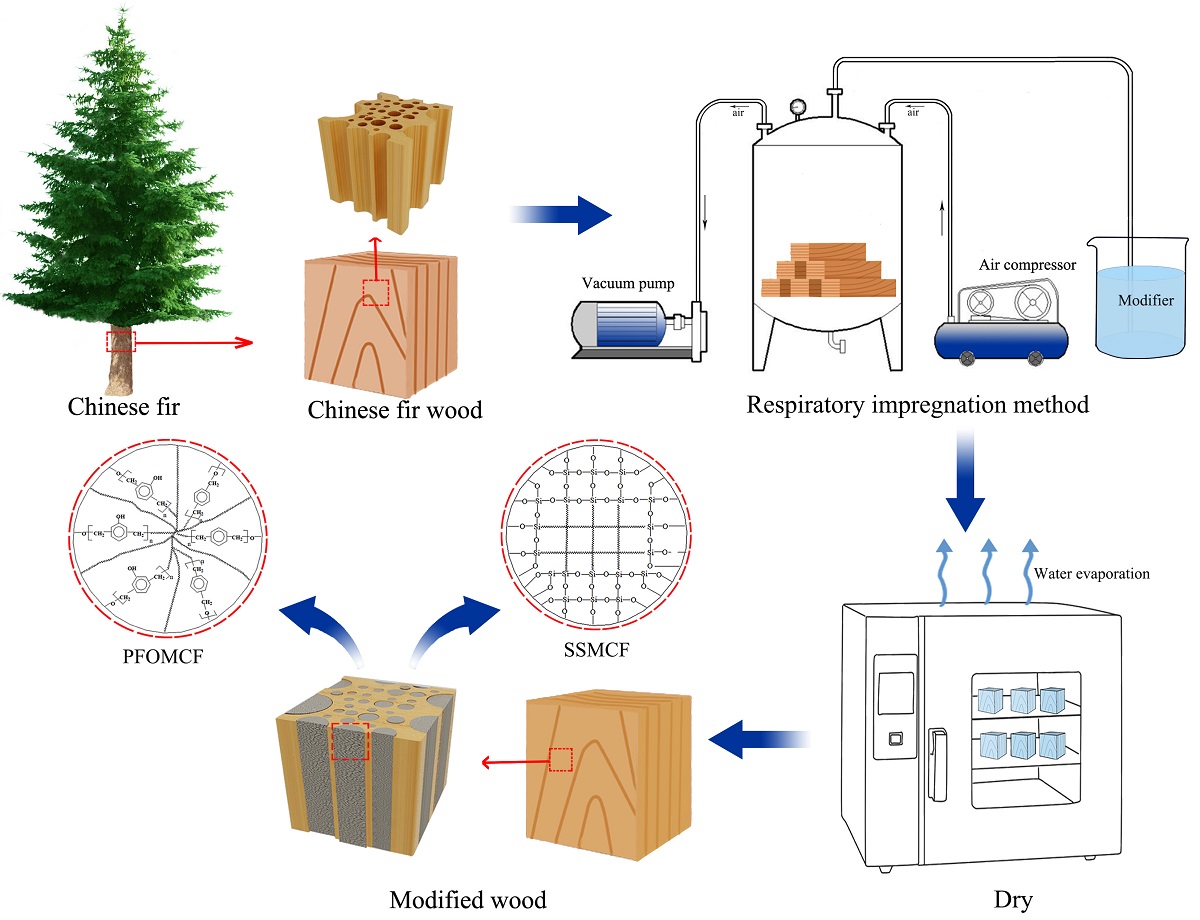
To compare The effects of organic and inorganic impregnation on the properties of unmodified, phenol formaldehyde oligomer-modified (PFOMCF), and sodium silicate-modified Chinese fir wood (SSMCF) were compared using samples prepared using the respiratory impregnation method. Impregnation and reinforcement effects and water resistance of PFOMCF and SSMCF were compared and the results was showed that the weight percentage gain, density increase rate, bending strength, and compressive strength of SSMCF were clearly higher than those of PFOMCF and had a lower water absorption rate within 60 h. The impregnation and reinforcement effects and dimensional stability of SSMCF were better than those of PFOMCF. FT-IR, XRD, CONE, and TGA examinations were used to test and analyze the chemical structure, crystalline structure, flame retardancy, and heat resistance of these modified woods. The results indicated that SSMCF possessed more hydrogen bonds than PFOMCF and that Si–O–Si chemical bonding with high bond energy was formed. Meanwhile, the weakened degree of the diffraction peak of SSMCF was much less than that of PFOMCF. These results explained that the mechanical properties and water resistance of SSMCF were better than PFOMCF. Compared with PFOMCF, SSMCF had a lower heat release rate (HRR), peak-HRR, mean-HRR, total heat release, smoke production rate, and total smoke production as well as higher thermal decomposition temperature and residual rate. Inorganic sodium silicate was shown to be a better flame retardant, while SSMCF had good smoke suppression effects, thermal stability, and safety performance in the case of fire.