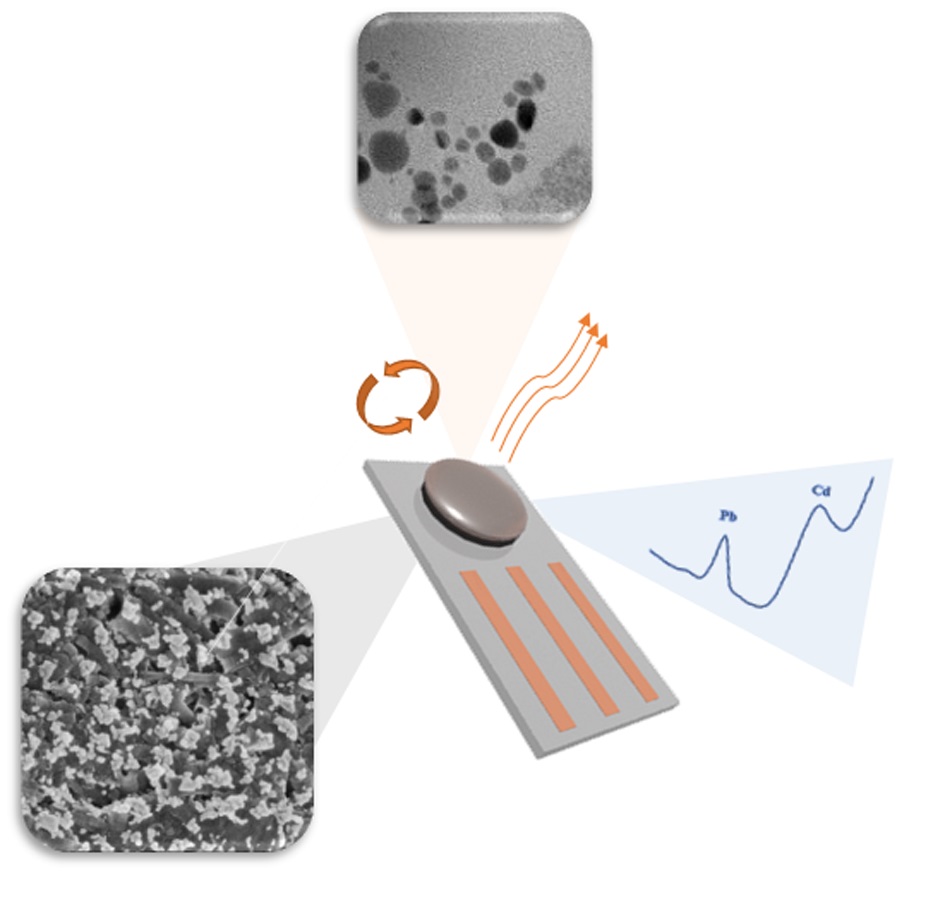
The screen-printed carbon nanofibers electrodes (SPCNFE) represent an alternative with great acceptance due to their results, as well as their low impact for the environment. In order to improve their performance, in the present work they were modified with silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) and electrochemically characterized by using anodic stripping voltammetry. From the Ag-NPs synthesis, silver seeds (Ag-NS) and silver nanoprisms (Ag-NPr) were obtained. The Ag-NPs formation was confirmed by micrographs where Ag-NPs with diameters of 12.20±0.04 nm for Ag-NS, and 20.40±0.09 nm for Ag-NPr were observed. The electrodes were modified by using three different deposition methods: drop-casting, spin-coating and in-situ approaches. It was observed that the last methodology showed a low amount of Ag-NS deposited on the electrode surface and a deep alteration of this surface. Those facts suggested that the in situ synthesis methodology were not appropriate for the determination of heavy metals and it was discarded. The incorporation of the nanoparticles by spin-coating and drop-casting strategies showed different spatial distribution on the electrode surface as proved by scanning electron microscopy. The electrodes modified by these strategies, were evaluated for the cadmium(II) and lead(II) detection using differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry, obtaining detection limit values of 2.1 and 2.8 µg L-1, respectively. The overall results showed that the incorporation route does not change directly the electrocatalytic effect of the nanoparticles, but the shape of these nanoparticles (spherical for seeds and triangular for prisms) has a preferential electrocatalytical enhancement over Cd(II) or Pb(II).