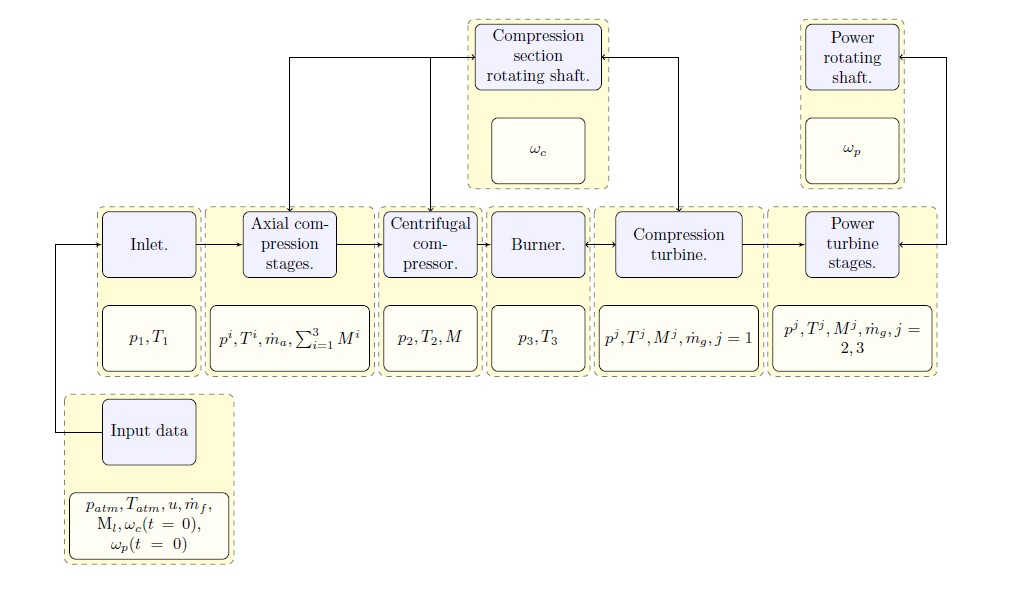
Instead of simplified steady-state models, with modern computers, one can solve the complete aero-thermodynamics happening in gas turbine engines. In the present article, we describe a mathematical model and numerical procedure to represent the transient response of a PT6A gas turbine engine operating at off-design conditions. The aero-thermal model consists of a set of algebraic and ordinary differential equations that arise from the application of the mass, linear momentum, angular momentum, and energy balances in each engine's component. The solution code has been developed in Matlab-Simulink using a block-oriented approach. Transient simulations of the PT6A engine start-up have been carried out by changing the original Jet-A1 fuel with biodiesel blends. Time plots of the main thermodynamic variables are shown, especially those regarding the structural integrity of the burner. Numerical results have been validated against reported experimental measurements and GasTurb simulations. The computer model has been capable to predict acceptable fuel blends, such that the real PT6A engine can be substituted to avoid the risk of damaging it.