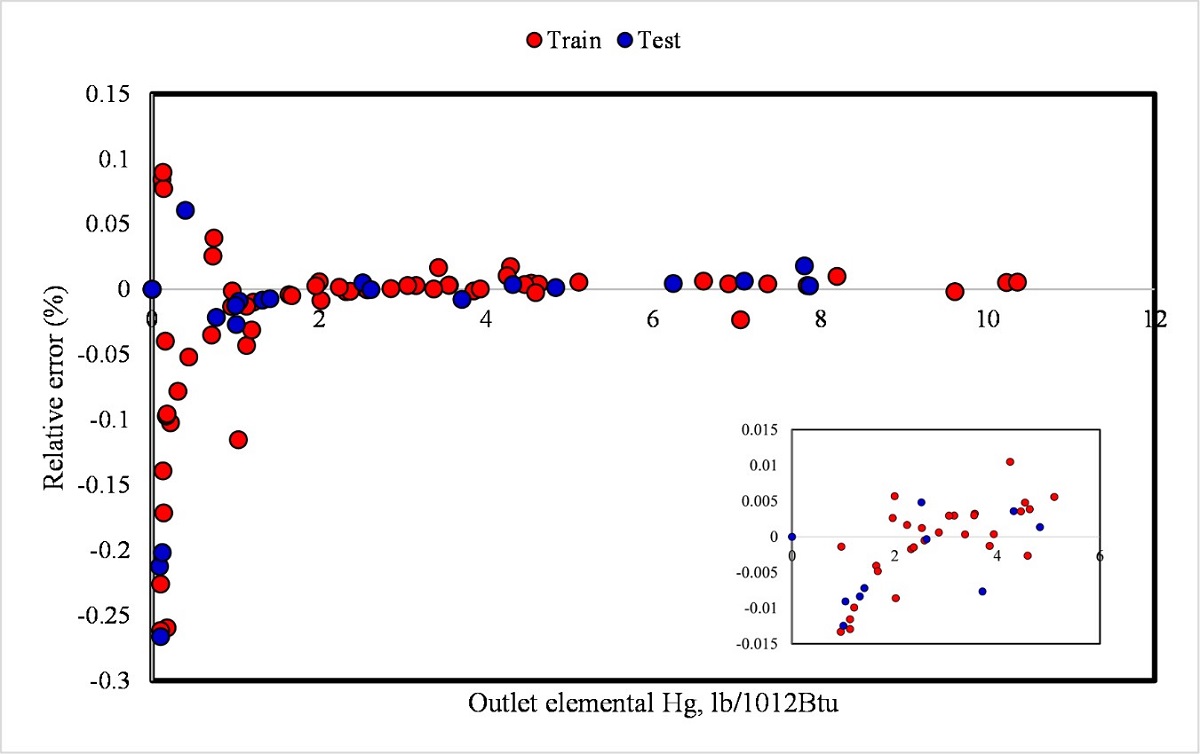
Accurate prediction of mercury content emitted from fossil-fueled power stations is of utmost importance for environmental pollution assessment and hazard mitigation. In this paper, mercury content in the output gas of power stations’ boilers was predicted using an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) method integrated with particle swarm optimization (PSO). The input parameters of the model include coal characteristics and the operational parameters of the boilers. The dataset has been collected from 82 power plants and employed to educate and examine the proposed model. To evaluate the performance of the proposed hybrid model of ANFIS-PSO model, the statistical meter of MARE% was implemented, which resulted in 0.003266 and 0.013272 for training and testing, respectively. Furthermore, relative errors between acquired data and predicted values were between -0.25% and 0.1%, which confirm the accuracy of the model to deal nonlinearity and representing the dependency of flue gas mercury content into the specifications of coal and the boiler type.