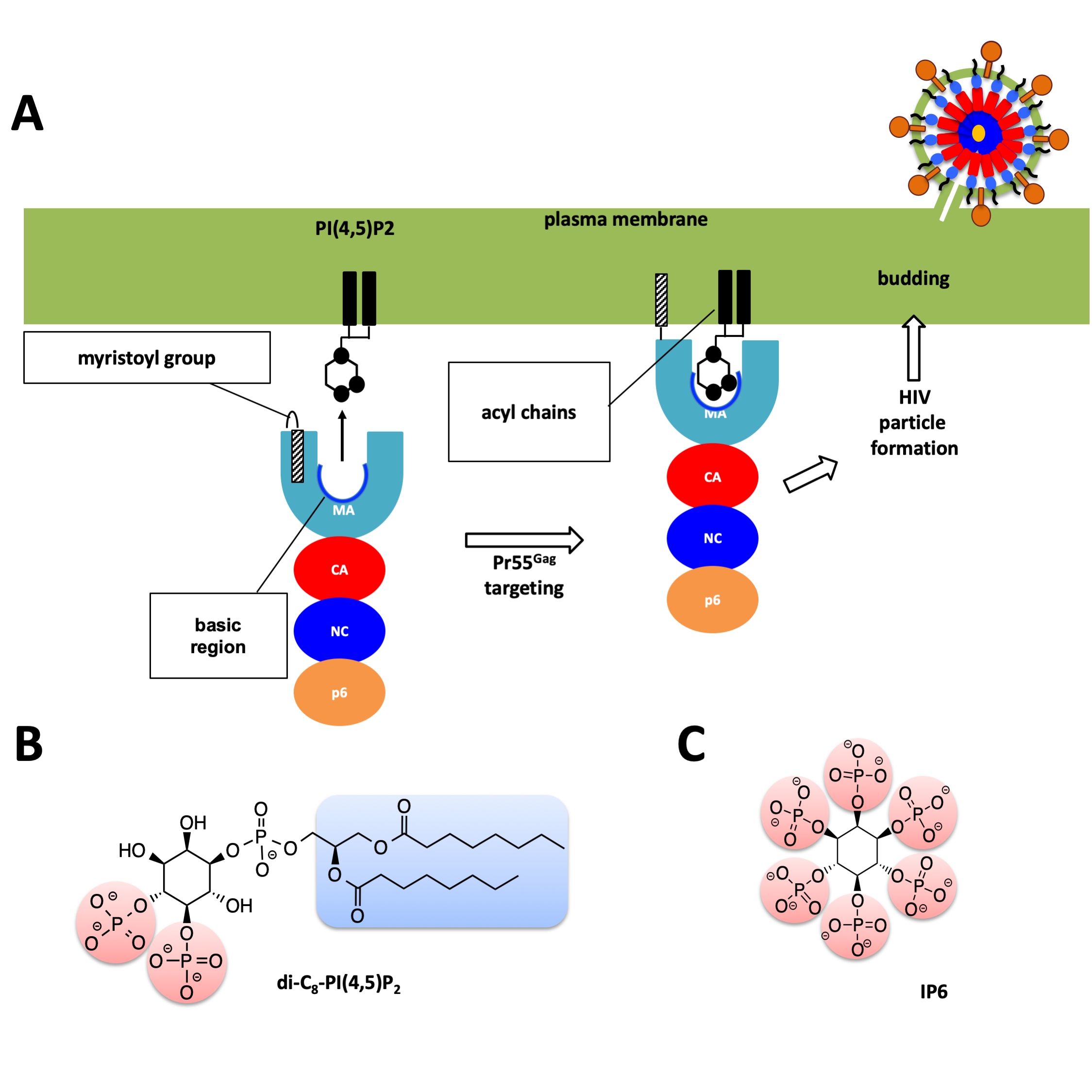
The Human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) matrix (MA) domain is involved in the highly regulated assembly process of the virus particles that occur at the host cell’s plasma membrane. High-resolution structures of the MA domain determined using cryo X-ray crystallography have provided initial insights into the possible steps in the viral assembly process. However, these structural studies have relied on large and frozen crystals in order to reduce radiation damage caused by the intense X-rays. Here, we report the first XFEL study of the HIV-1 MA domain’s interaction with inositol hexaphosphate (IP6), a phospholipid headgroup mimic. We also describe the purification, characterization and microcrystallization of two MA crystal forms obtained in the presence of IP6. In addition, we describe the capabilities of serial femtosecond X-ray crystallography (SFX) using X-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) to elucidate the diffraction data of MA-IP6 complex microcrystals in liquid suspension at ambient temperature. Two different microcrystal forms of MA-IP6 complex both diffracted to beyond 3.5 Å resolution, demonstrating the feasibility of using SFX to study the complexes of MA domain of HIV-1 Gag polyprotein with IP6 at near-physiological temperatures. Further optimization of the experimental and data analysis procedures will lead to better understanding of the MA domain of HIV-1 Gag and IP6 interaction at high resolution and provide basis for optimization of the lead compounds for efficient inhibition of the Gag protein recruitment to the plasma membrane prior to virion formation.