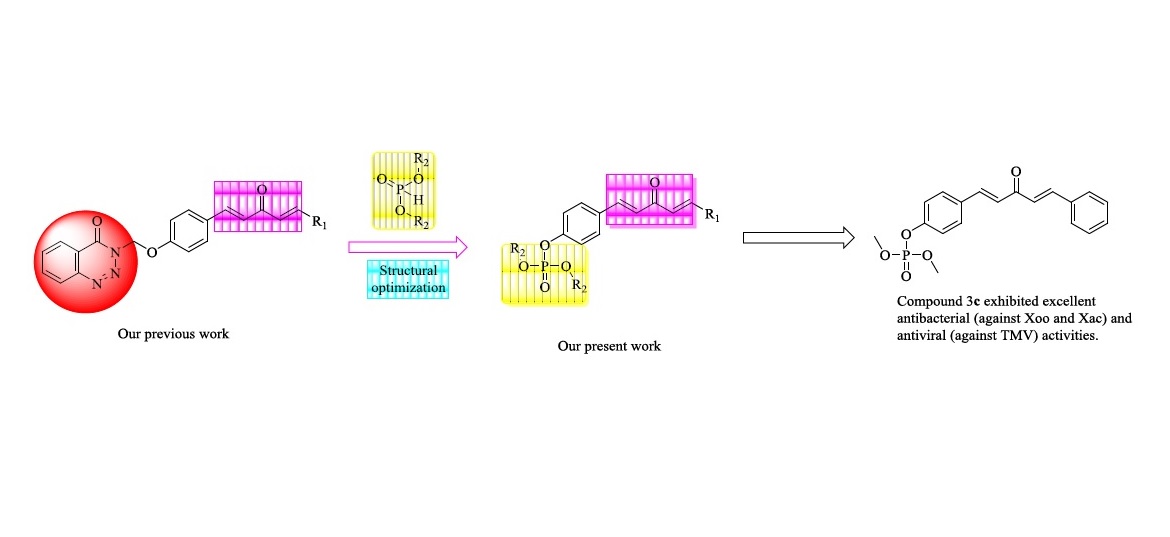
A series of penta-1,4-dien-3-one containing a H-phosphonate scaffold were designed and synthesized. The structures of all title compounds were determined by 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, 31P-NMR, and HRMS. Bioassay results showed that several of the title compounds exhibited remarkable antibacterial and antiviral activities. Among these, compounds 3c and 3o exhibited substantial antibacterial activities against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae (Xoo) and Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri (Xac). In addition, compounds 3c, 3f, and 3r showed remarkable curative activities against tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), with 50% effective concentration (EC50) values of 290.0, 234.0, and 373.6 μg/mL, respectively. These were superior to that of ningnanmycin (386.2 μg/mL). Compound 3r exhibited comparative protective activity against TMV, with an EC50 value of 291.1 μg/mL, which was better than that of ningnanmycin (297.1 μg/mL). Notably, the solubility of all title compounds improved relative to the lead compound curcumin. These results suggest that penta-1,4-dien-3-one containing a H-phosphonate scaffold may be considered as an activator for antibacterial and antiviral agents.