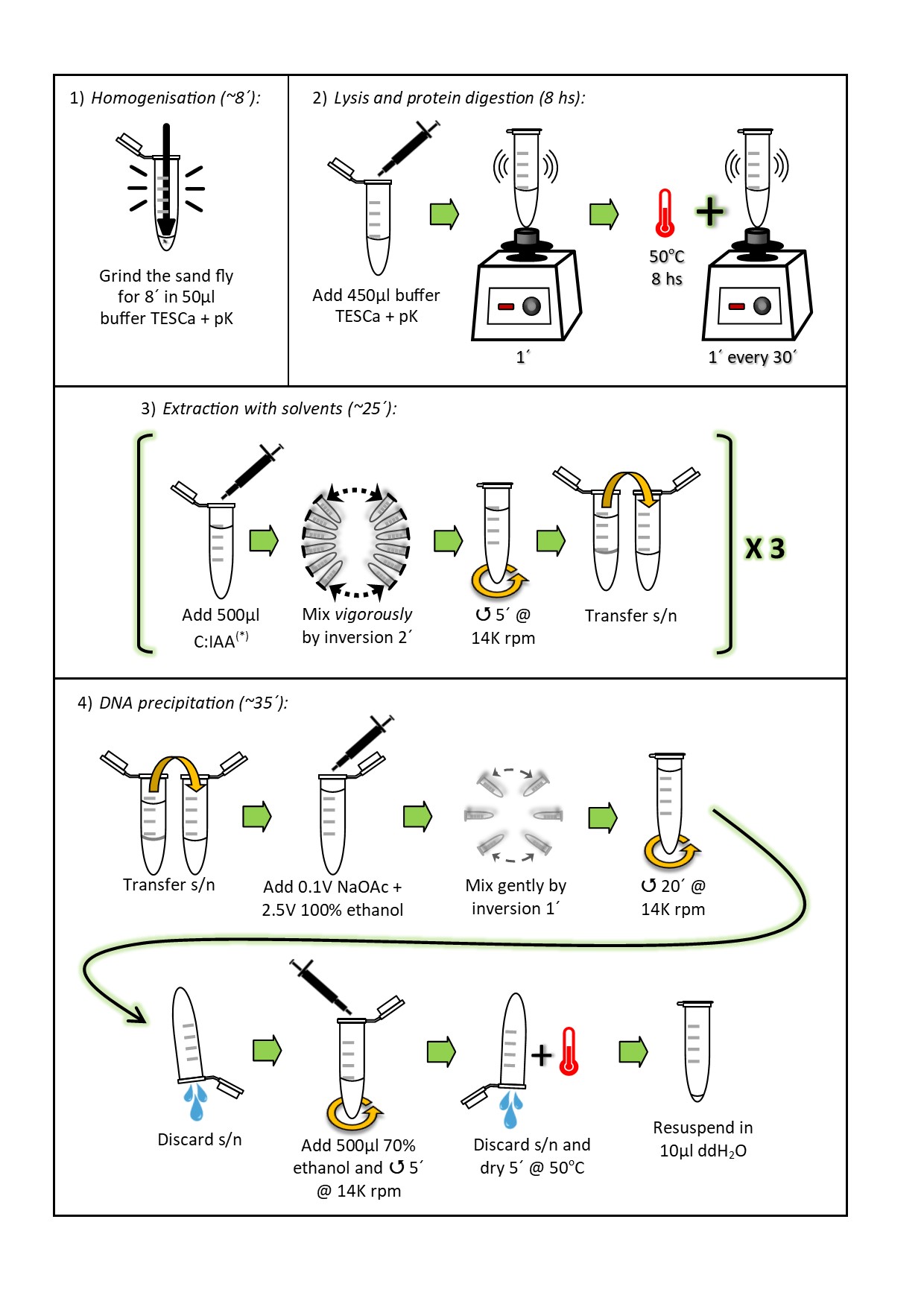
Numerous protocols have been published for extracting DNA from phlebotomines. Nevertheless, their small size is generally an issue in terms of yield, efficiency, and purity, for large-scale individual sand fly DNA extractions when using traditional methods. Even though this can be circumvented with commercial kits, these are generally cost-prohibitive for developing countries. We encountered these limitations when analysing parasite infection in Lutzomyia spp. by PCR [1] and, for this reason, we evaluated various modifications on a previously published protocol ([2] and Acardi personal communication). The most significant variation was the use of a different lysis buffer [3] to which added Ca2+ (buffer TESCa), because this ion protects proteinase K against autolysis, increases its thermal stability, and could have a regulatory function for its substrate-binding site [4]. Individual sand fly DNA extraction success was confirmed by amplification reactions using internal control primers that amplify a fragment of the cacophony gene [5,6]. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time a lysis buffer containing Ca2+ has been reported for the extraction of DNA from sand flies.