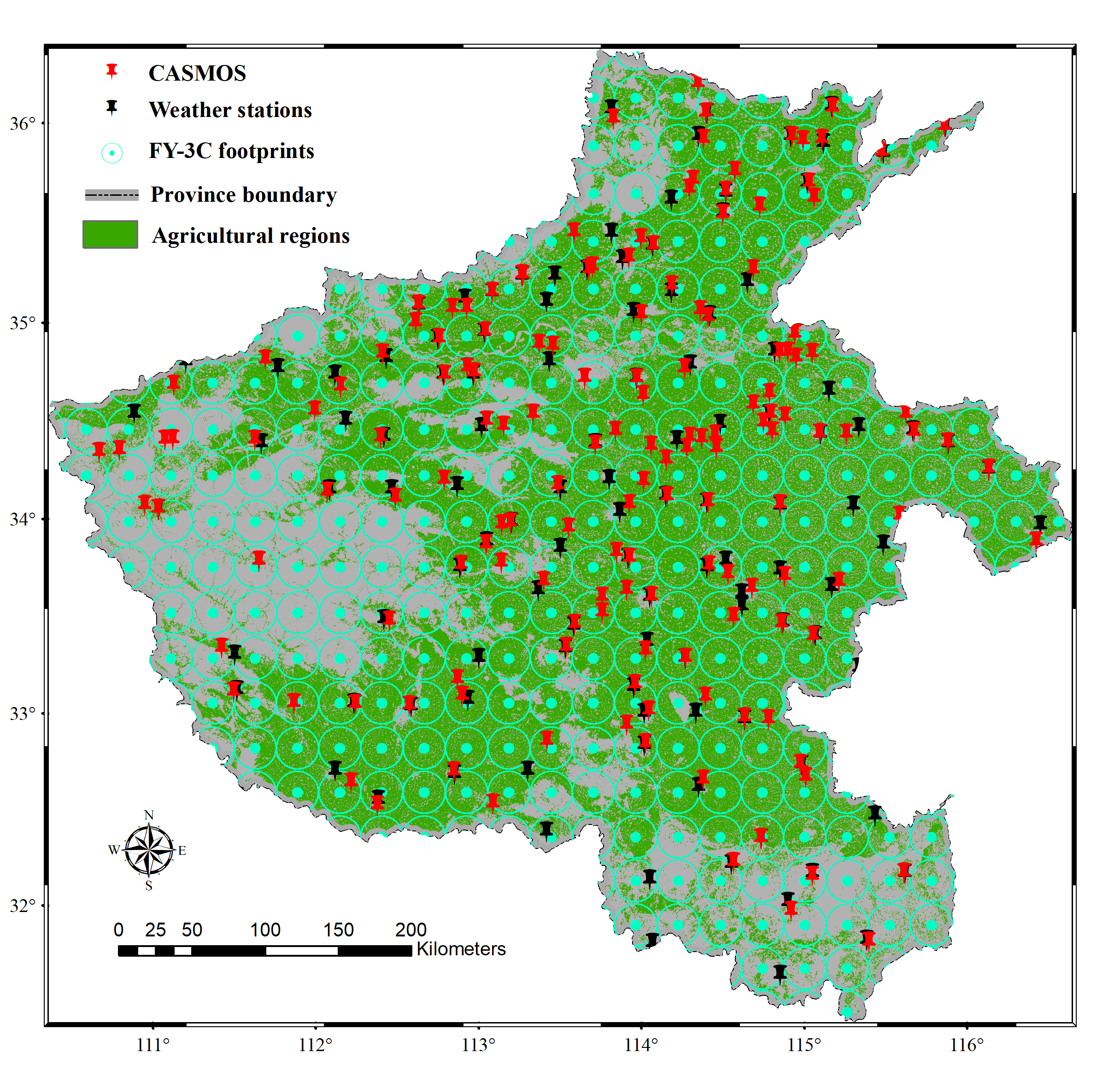
Soil moisture (SM) products derived from passive satellite missions are playing an increasingly important role in agricultural applications, especially in crop monitoring and disaster warning. Evaluating the dependability of those products before they can be used on a large scale is crucial. In this study, we assessed the level 2 (L2) SM product from the Chinese Fengyun-3C (FY-3C) radiometer against in situ measurements collected from the Chinese Automatic Soil Moisture Observation Stations (CASMOS) during a one-year period from January 1 to December 31, 2016 in Henan, which is an agricultural province in China. Four statistical parameters were used to evaluate the products’ reliability: mean difference, root-mean-square error (RMSE), unbiased RMSE (ubRMSE), and the correlation coefficient. These statistical indicators revealed that the FY-3C L2 SM product generally did not agree with the in situ SM data from CASMOS. The time-series analysis further indicated that the correlations and estimated error were highly related to the growing periods of the crops in our study area. FY-3C L2 SM data tended to overestimate soil moisture during May, August, and September, when the crops reach their maximum vegetation density, and tended to underestimate the soil moisture content during the rest of the year. The averaged correlation coefficient between FY-3C SM and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) normalized difference vegetation index was 0.55, which demonstrates that the vegetation water content of the crops considerably influences the SM product. To improve the accuracy of the FY-3C SM product, an improved algorithm that can filter out the influences of the crops should be applied in the future.