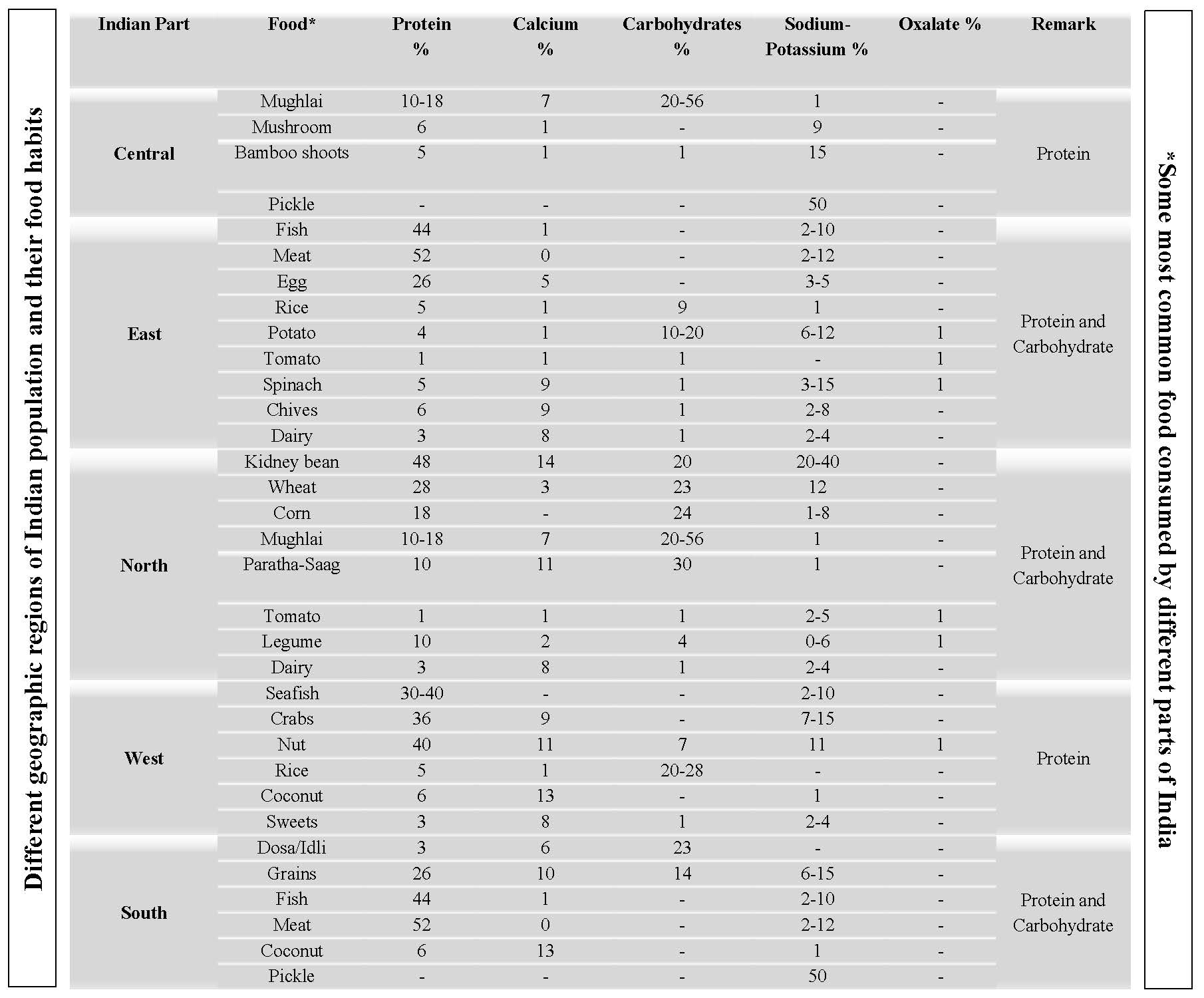
Food intake plays a pivotal role of human growth, which necessarily contributes 45% of global economy and wellbeing in general. Consumption of balanced food is elementary for overall good health while a shift of equilibrium can lead to malnutrition, prenatal death, obesity, osteoporosis and bone fractures, coronary heart diseases (CHD), idiopathic hypercalciuria, diabetes and many more. Though CHD, osteoporosis, malnutrition, obesity are being classified thoroughly in the literature, there are fragmented findings in the regime of kidney stone diseases (KSD) and the correlation with food intake therein. KSD associated with hematuria and renal failure poses an increasing threat to the healthcare and global economy while its emergence of Indian populations is being affected with multi-factorial urological disorder resulting from several factors. In this realm, epidemiological, biochemical, macroeconomic situations been portrayed when food intake is also a paramount importance which rarely been forecasted. Hence, in this article we will be reviewing the corollary connotation with diverse food consumption and the efficacy it plays in KSD extrapolating in Indian context.