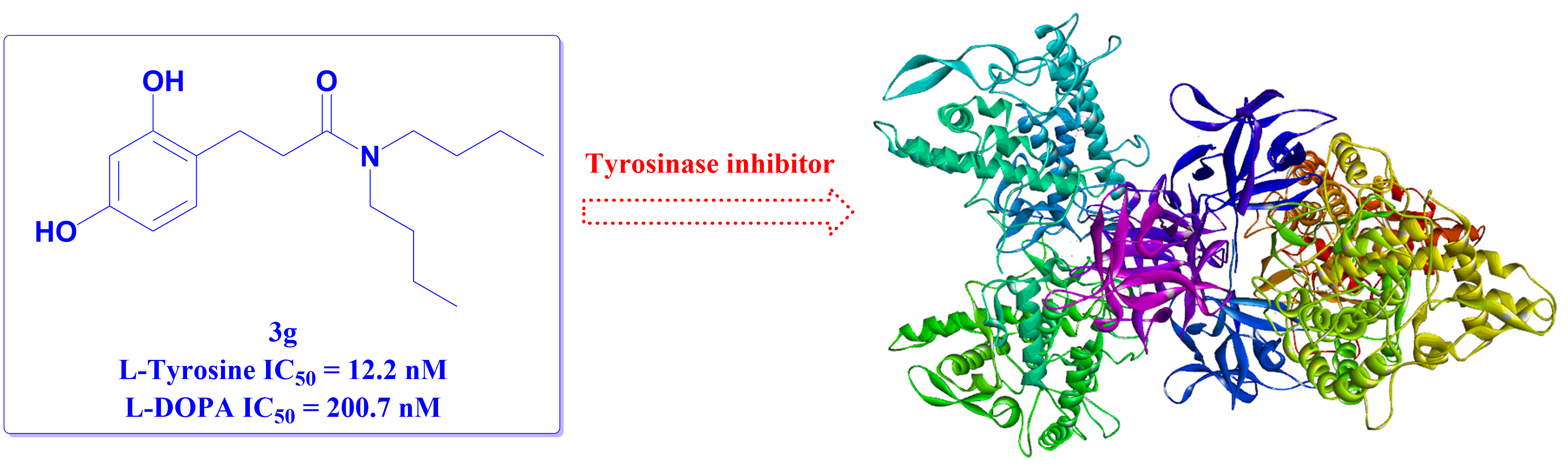
Compounds with tyrosinase inhibitory efficacy could be effective as depigmenting agents. Although a large number of natural and synthetic tyrosinase inhibitors have been reported, few of them are used as skin-whitening agents due to poor activity and safety concerns. 3-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)propionic acid (DPPA), a naturally occurring compound isolated from Ficus carica, was previously discovered as a moderate tyrosinase inhibitor. In this study, the structure-activity relationship study of DPPA was conducted. Compound 3g, with the 2,4-resorcinol subunit and terminal hydrophobic di-butylamino group, was identified with low nanomolar enzymatic IC50 value. Additionally, compound 3g could effectively reduce melanin levels in B16-F10 melanoma cells treated with α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) without affecting cell viability and proliferation. All these results indicated that compound 3g could be considered as a promising candidate for the treatment of diseases associated with hyperpigmentation.