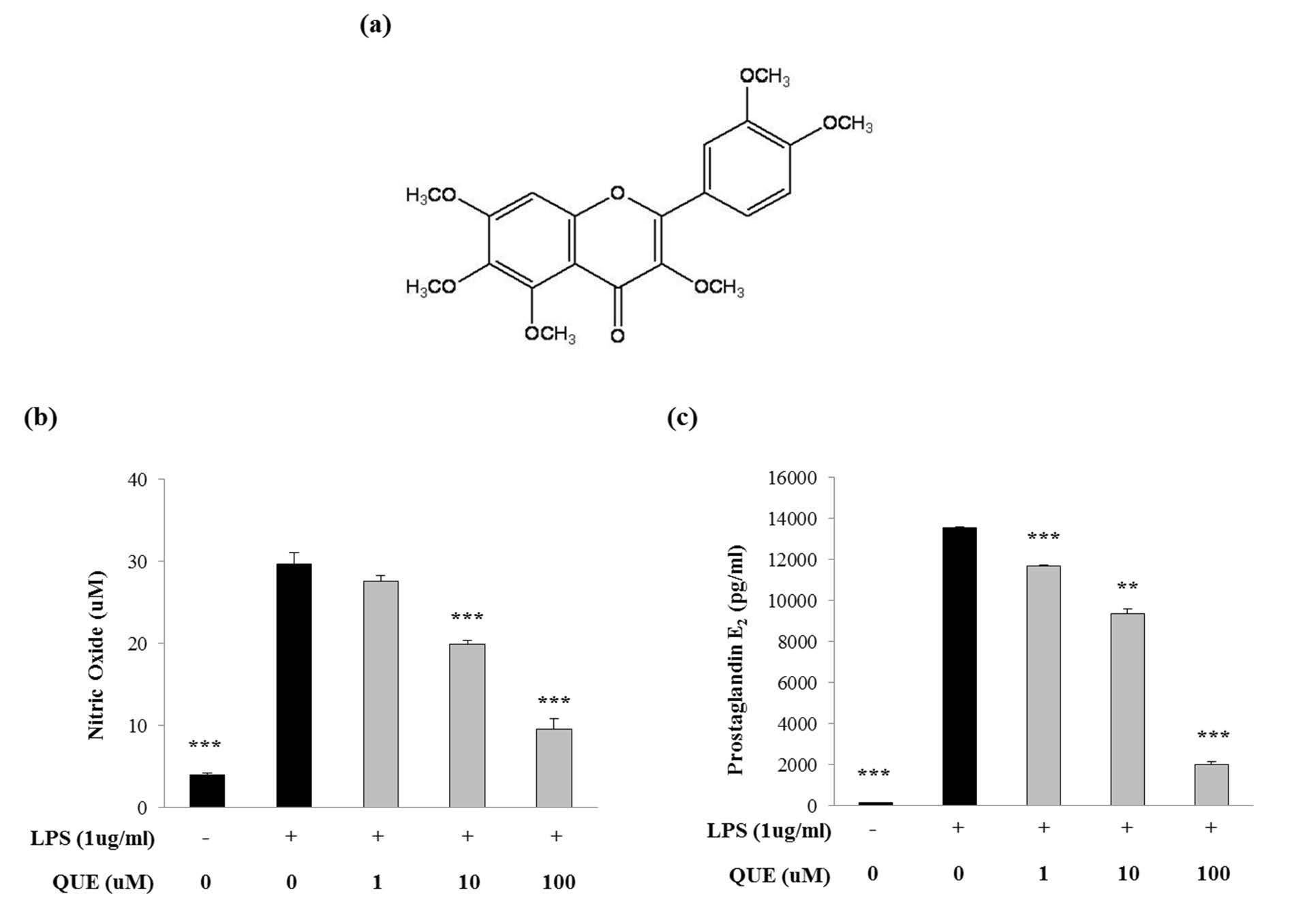
Citrus peel has been used in Asian traditional medicine for the treatment of cough, asthma, and bronchial disorders. However, the anti-inflammatory effect of quercetogetin (QUE), a polymethoxylated flavone isolated from the peel of citrus unshui is poorly understood. We investigated the anti-inflammatory effect and the molecular mechanisms of QUE in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW264.7 cells. QUE inhibited the production of NO and prostaglandin E2 by suppressing the LPS-induced expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 at both the mRNA and protein levels. QUE suppressed the production of proinflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α. QUE also inhibited the translocation of the nuclear factor kappa B subunit, p65, into the nucleus by interrupting the phosphorylation of IκB-α in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Based on the finding that QUE significantly decreased p-ERK protein expression in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells, we confirmed that suppression of the inflammatory process by QUE was mediated through the MAPK pathway. This is the first report on the strong anti-inflammatory effects of QUE, which is a compound that can potentially be used as a therapeutic agent for inflammatory diseases.