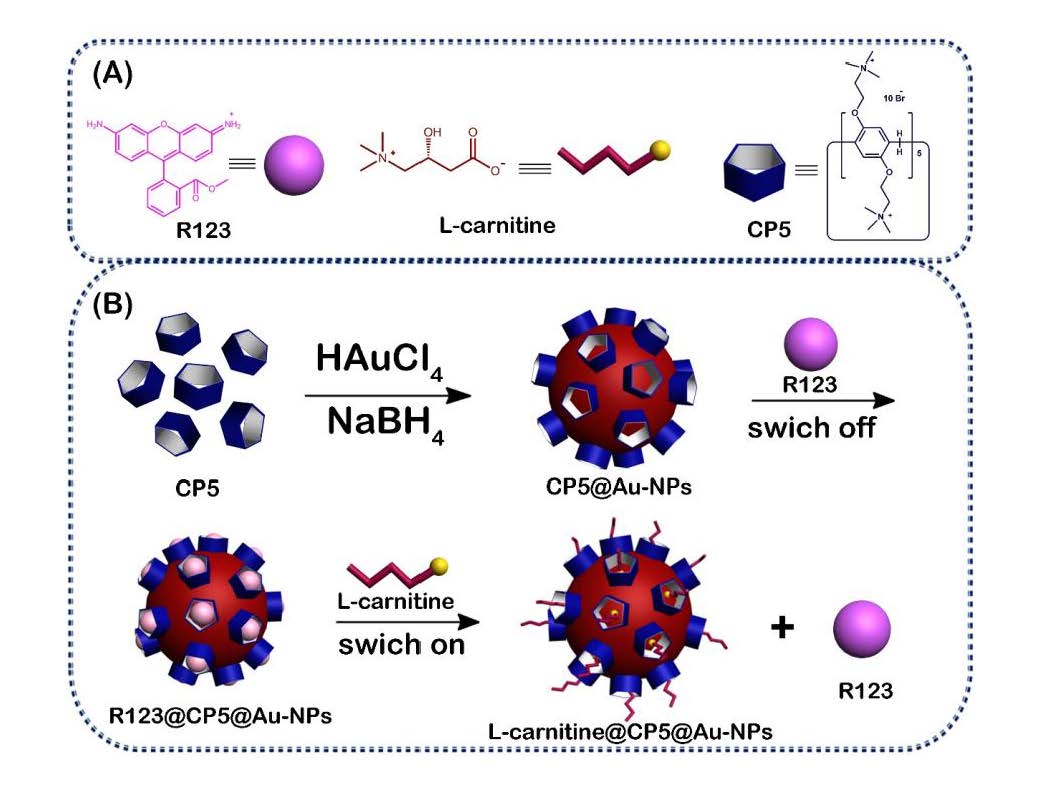
A supramolecular host-guest interaction and sensing between cationic pillar[5]arenes (CP5) and L-carnitine were developed by the competitive host-guest recognition for the first time. The fluorescence sensing platform was constructed by CP5 functionalized Au nanoparticles (PP5@Au-NPs) as receptor and probe (rhodamine 123, R123), which shown a high sensitivity and selectivity to L-carnitine detection. Due to the property of the negative charge and molecular size of L-carnitine, it can be highly captured by the CP5 via electrostatic interactions and hydrophobic interactions. The mechanism of host-guest between PP5 and L-carnitine was studied by 1H NMR and molecular docking, which indicated more affinity binding force of PP5 with L-carnitine. Therefore, a selective and sensitive fluorescent method was developed. It has a linear response of 0.1–2.0 and 2.0–25.0 μM and a detection limit of 0.067 μM (S/N = 3) for L-carnitine. The fluorescent sensing platform was also used to detect L-carnitine in human serum and milk samples, which provided potential applications of detection drugs of abuse, and had path for guarding a serious food safety issues.