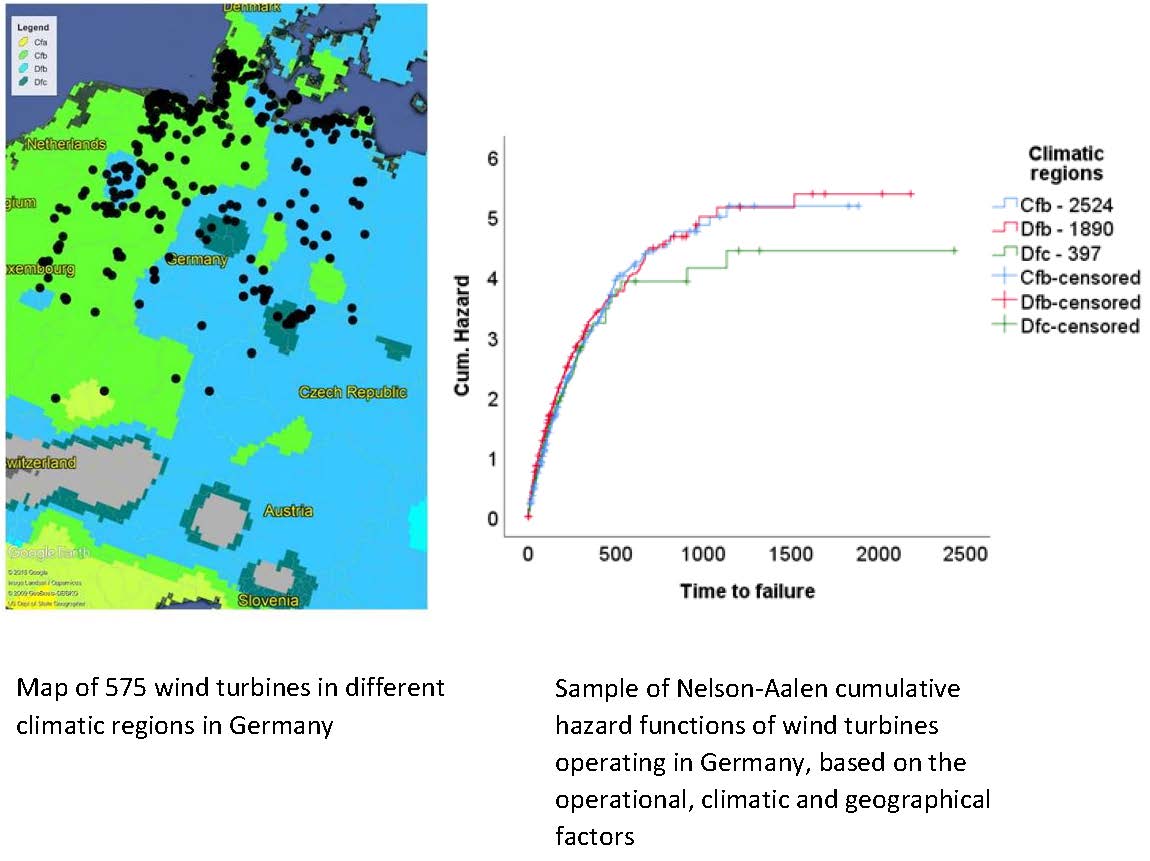
Failure of wind turbines is a multi-faceted problem and its monetary impact is often unpredicted. In this study, we present a novel application of survival analysis on wind turbine reliability performance that includes accounting of previous failures and history of scheduled maintenance. We investigate the operational, climatic and geographical factors which affect wind turbine failures and model the risk rate of wind turbine failures based on data from 109 turbines in Germany operating during a period of 19 years. Our analysis showed that adequately scheduled maintenance can increase the survivorship of wind turbine systems and electric subsystems up to 2.8 and 3.8 times, respectively compared to the ones without scheduled maintenance. Geared-drive wind turbines and their electrical systems were observed to have 1.2- and 1.4-times higher survivorship, respectively, compared to direct-drive turbines and their electrical systems. It is also found that survivorship of frequently-failed wind turbine components, such as switches, is worse in geared-drive than in direct-drive wind turbines. We show that survival analysis is a useful tool for guiding the reduction of operating and maintenance costs of wind turbines.