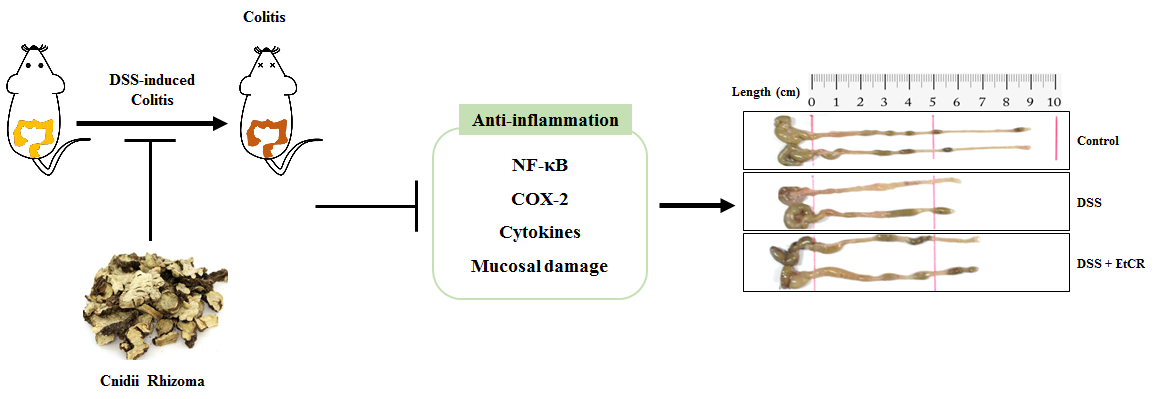
In this study, dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced in vivo model and LPS-stimulated in vitro model were used to confirm whether ethanol extract of Cnidii Rhizoma (EtCR) could ameliorate UC. EtCR improved symptoms of UC, including body weight loss, colon length shortening, disease activity index (DAI), and colon mucosal damage. In addition, EtCR decreased inflammatory mediators, including cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), in colon tissue. To further confirm the UC improving mechanism, RAW 264.7 cells and HT29 human epithelial cells were used. EtCR reduced expression of inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6) and inflammatory mediators (nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2) via JNK and NF-κB signaling pathway in RAW 264.7 cells. In addition, EtCR increased expression of trefoil factor 3 (TFF3), which is an epithelial cell protective factor, in HT29 cells. Taken together, our study suggests that EtCR has treatment effect on UC and can be a therapeutic agent.