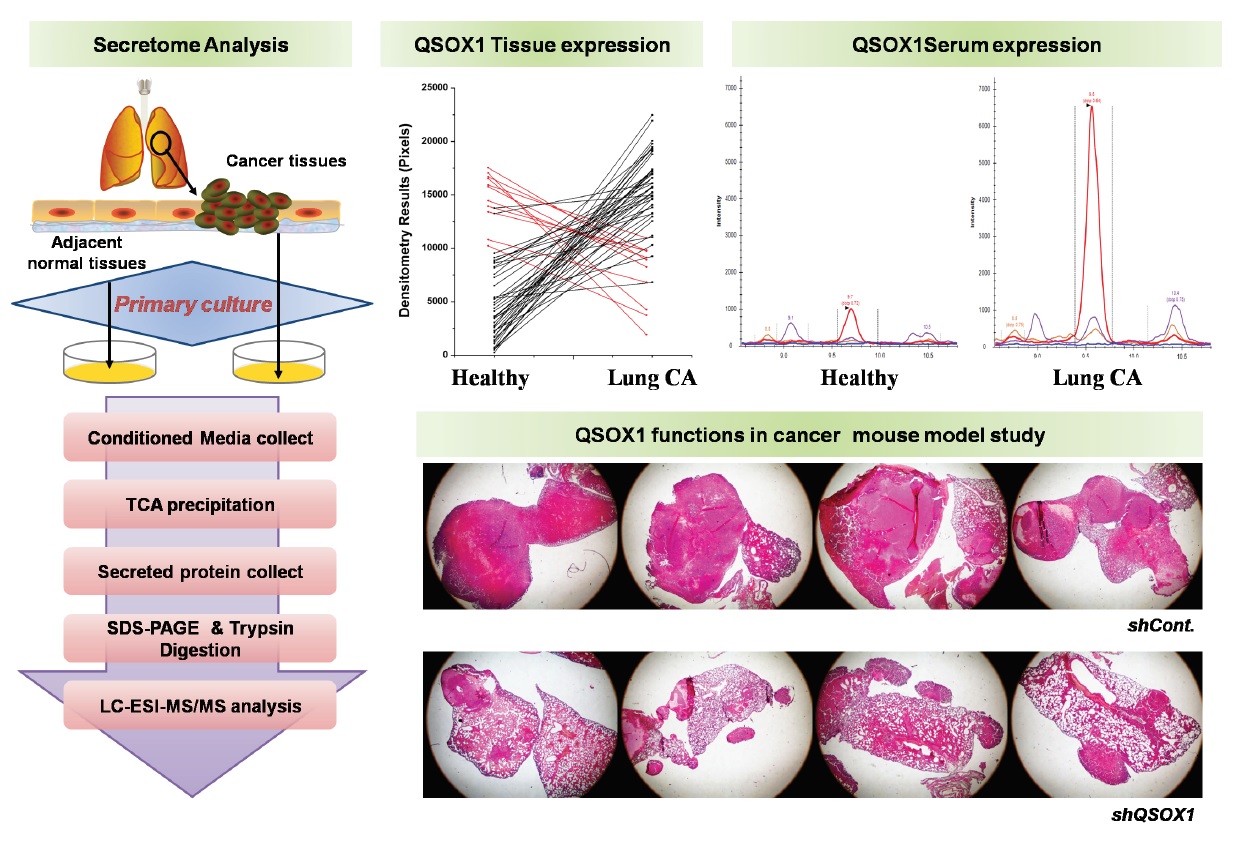
As lung cancer shows the highest mortality in cancer related death, serum biomarkers are demanded for the lung cancer diagnosis and its treatment. To discover lung cancer protein biomarkers, secreted proteins from primary cultured lung cancer and adjacent normal tissues from patients were subjected to LC/MS-MS proteomic analysis. Quescin sulfhydryl oxidase(QSOX1) was selected as a biomarker candidate from the proteins enriched in the secretion of lung cancer cells. QSOX1levels were higher in 82% (51 of 62 tissues) of lung cancer tissues compared to adjacent normal tissues. Importantly, QSOX1 serum levels were significantly higher in cancer patients (p<0.05, AUC=0.89), when measured by multiple reaction monitoring(MRM). Higher levels of QSOX1 are also uniquely detected in lung cancer tissues among several other solid cancers by immunohistochemistry. QSOX1 knock-downed Lewis lung cancer (LLC) cells was less viable from oxidative stress and had reduced migration and invasion. In addition, LLC mouse models with QSOX1 knock-down also proved that QSOX1 functions in promoting cancer metastasis. In conclusion, QSOX1 might be a lung cancer tissue-derived biomarker and involved in the promotion of lung cancers, and thus can be a therapeutic target for lung cancers.