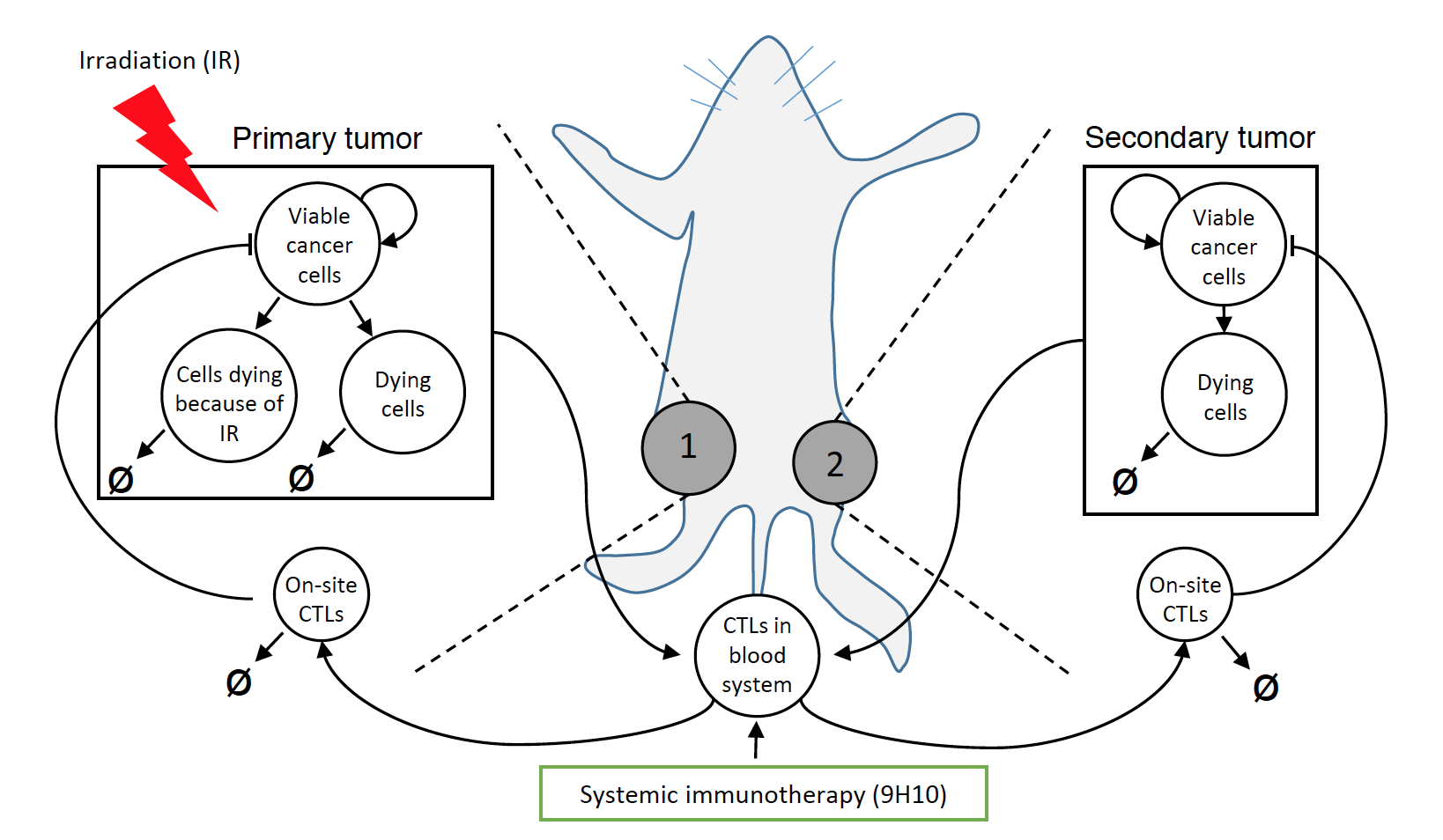
Synergy of radiation and immune system is currently receiving significant attention in oncology as numerous studies have shown that cancer irradiation can induce strong antitumor immune responses. It remains unclear, however, what are the best radiation fractionation protocols to maximize the therapeutic benefits of this synergy. Here, we present a novel mathematical model that can be used to predict and dissect the complexity of the immune-mediated response at multiple tumor sites after applying focal irradiation and systemic immunotherapy. We successfully calibrate the proposed framework with published experimental data, in which two tumors were grown in mice at two spatially separated sites from which only one was irradiated using various radiation fractionation protocols with and without concurrent systemic immunotherapy. The proposed model is calibrated to fit the temporal dynamics of tumor volume at both sites and can predict changes in immune infiltration in the non-irradiated tumors. The model was then used to investigate additional radiation fractionation protocols. Model simulations suggest that the optimal radiation doses per fraction to maximize antitumor immunity are between 10-13 Gy, at least for the experimental setting used for model calibration. This work provides the framework for evaluating radiation fractionation protocols for radiation-induced immune-mediated systemic antitumor responses.