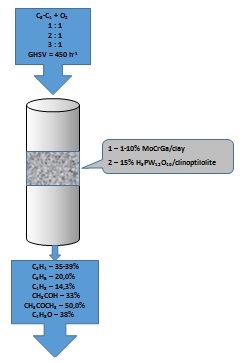
The processing of alkanes (the main components of natural gas) for obtaining of industrially important chemical products is one of the most urgent environmental problems, because the major share of raw materials are burned in torches. Therefore, the main goal of the work is the development of catalysts and conditions for obtaining of important petrochemical products from light alkanes. For the preparation of catalysts, Mo, Cr and Ga oxide catalysts as well as catalysts based on heteropoly compounds, supported on natural materials were used. The catalysts were prepared by the capillary impregnation method and used in oxidative conversion in a flowing unit while varying the process conditions. It has been determined that 5 and 10% MoCrGa catalysts are optimal for obtaining of liquid and gaseous products, and 1% catalyst is more favorable for the synthesis of gaseous products. Supported catalysts from heteropoly acid Н3PW12O40 are highly active in oxidative dehydrogenation and cracking processes, which are concurrent. High activity is caused by dispersity of catalysts, formation of crystal hydrates and amorphous phase of heteropoly acid in a condition of interaction with carrier. Maximum yield of C2H4 - 35.2% at 973 K, C3H6 – 20.0% and C4H8 – 14.3% at 773 К were observed.