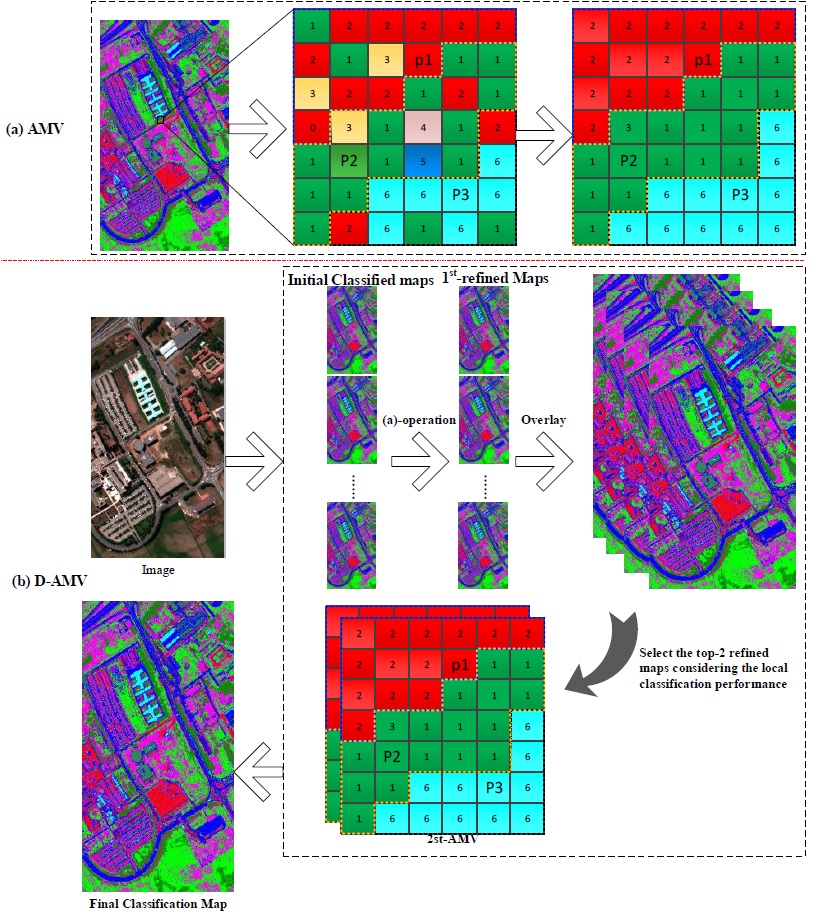
Land-cover classification that uses very-high-resolution (VHR) remote sensing images is a topic of considerable interest. Although many classification methods have been developed, there is still room for improvements in the accuracy and usability of classification systems. In this paper, a novel post-processing approach based on a dual-adaptive majority voting strategy (D-AMVS) is proposed for improving the performance of initial classification maps. D-AMVS defines a strategy for refining each label of a classified map that is obtained by different classification methods from the same original image and fusing the different refined classification maps to generate a final classification result. The proposed D-AMVS contains three main blocks. 1) An adaptive region is generated by extending gradually the region around a central pixel based on two predefined parameters (T1 and T2) in order to utilize the spatial feature of ground targets in a VHR image. 2) For each classified map, the label of the central pixel is refined according to the majority voting rule within the adaptive region. This is defined as adaptive majority voting (AMV). Each initial classified map is refined in this manner pixel by pixel. 3) Finally, the refined classified maps are used to generate a final classification map, and the label of the central pixel in the final classification map is determined by applying AMV again. Each entire classified map is scanned and refined pixel by pixel based on the proposed D-AMVS. The accuracies of the proposed D-AMVS approach are investigated through two remote sensing images with high spatial resolutions of 1.0 and 1.3 m, respectively. Compared with the classical majority voting method and a relatively new post-processing method called general post-classification framework, the proposed D-AMVS can achieve a land-cover classification map with less noise and higher classification accuracies.