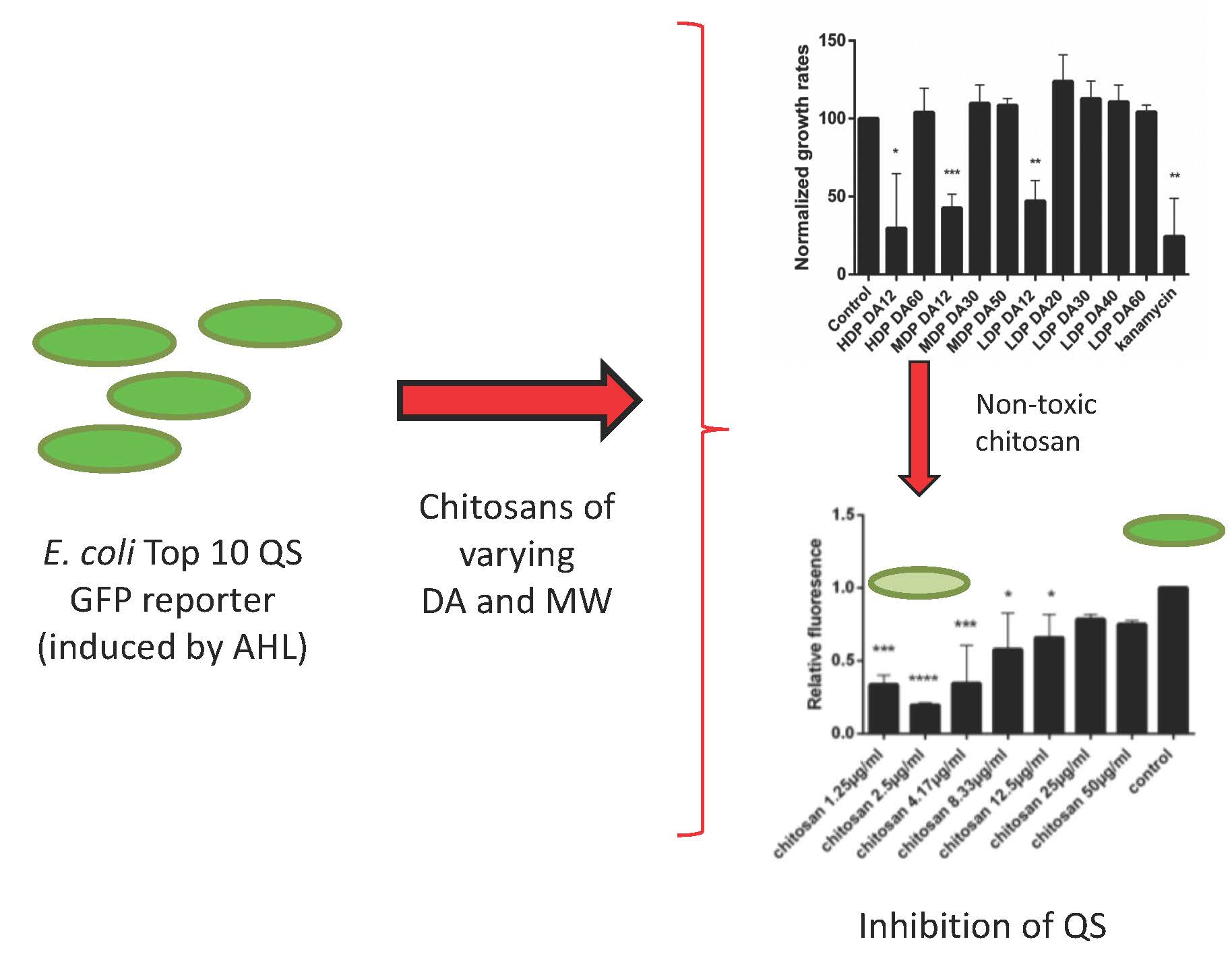
New approaches to deal with drug-resistant pathogenic bacteria are urgent. We studied the antibacterial effect of chitosans against an E. coli quorum sensing biosensor reporter strain, and selected a non-toxic chitosan to evaluate its QS inhibition activity and its effect on bacterial aggregation. To this end, chitosans of varying DA (12 to 69%) and Mw (29 to 288 KDa) were studied. Only chitosans of low DA (~12%) inhibited the bacterial growth, regardless of the Mw. Chitosan MDP DA30 (DA 42% and Mw 115 kDa) was selected for further QS inhibition and SEM imaging studies. MDP DA30 chitosan exhibited QS inhibition activity in an inverse dose-dependent manner (≤12.5 µg/mL). SEM images revealed that this chitosan, when added at low concentration (≤30.6 µg/mL), induced substantial bacterial aggregation, whereas at high concentration (234.3 µg/mL), it did not. Aggregation explains the QS inhibition activity as the consequence of retardation of the diffusion of AHL.