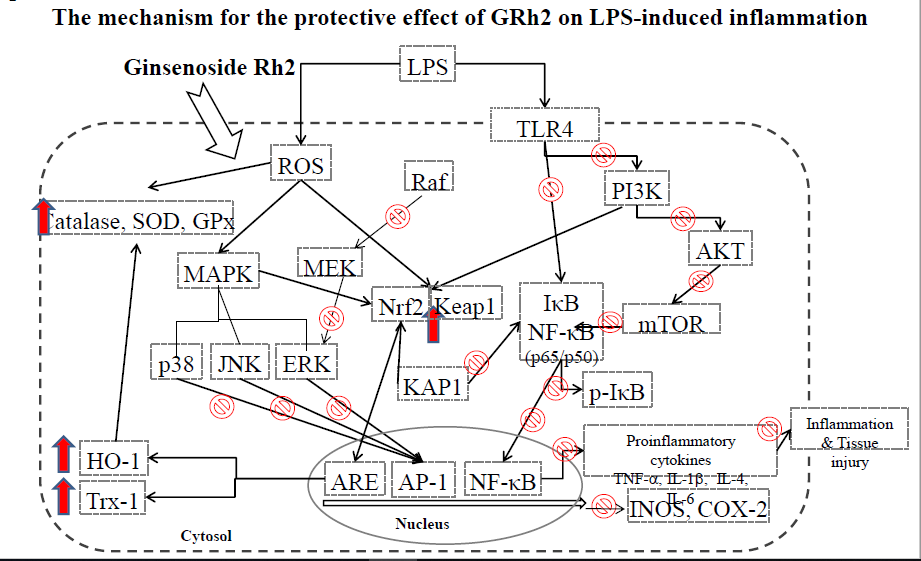
The anti-inflammatory effect of ginsenoside Rh2 (GRh2) is one of the most important ginsenosides. The purpose of this study is to identify the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of GRh2 after LPS challenge lung injury animal model. GRh2 reduced LPS-induced NO, TNF-α, IL-1, IL-4, IL-6 and IL-10 productions in lung tissues. GRh2 treatment decreased the histological alterations in the lung tissues and BALF protein content and total cells number also diminished in LPS-induced lung injury mice. Moreover, GRh2 blocked iNOS, COX-2, the phosphorylation of IκB-α, ERK, JNK, p38, Raf-1 and MEK protein expression which is corresponded to the growth of HO-1, Nrf-2, catalase, SOD and GPx expressions in LPS-induce lung injury. An experimental study has suggested that GRh2 has provided with anti-inflammatory effects in vivo, and its potential therapeutic efficacy in major anterior segment lung diseases.