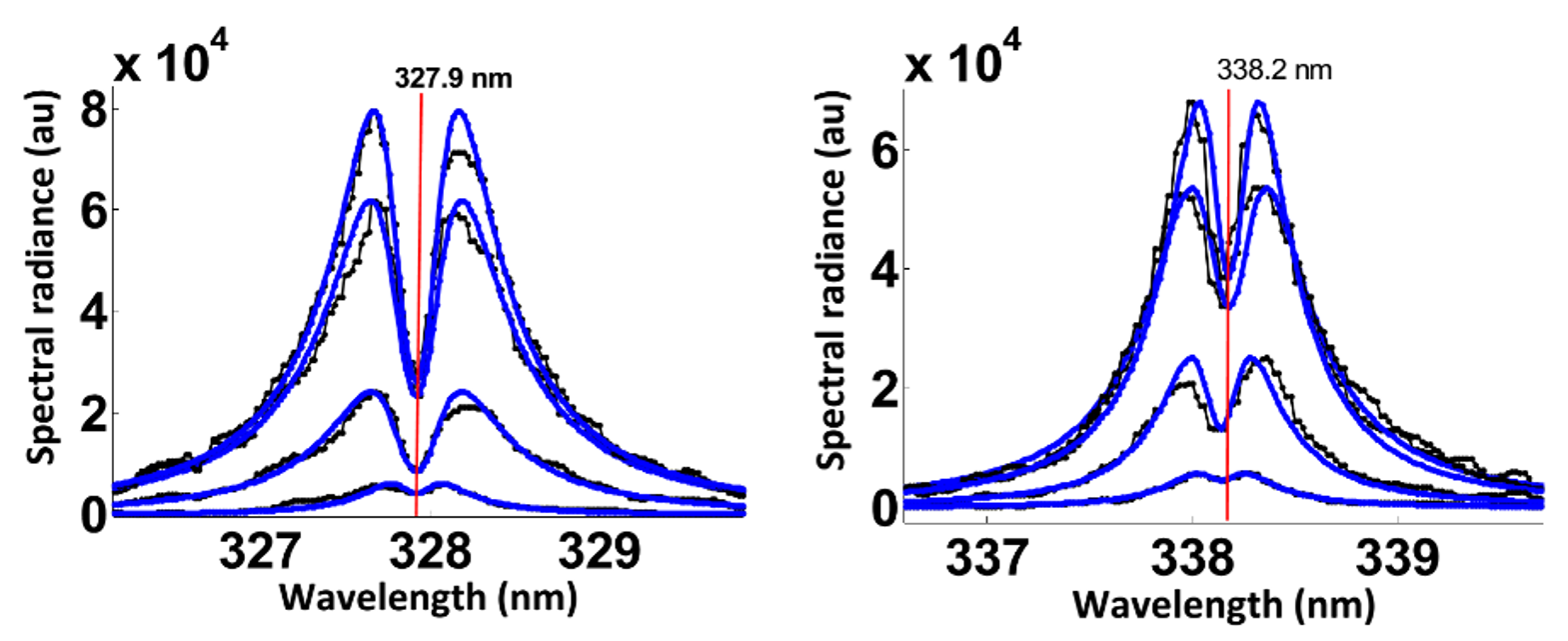
The resonance spectra of neutral silver indicate self-absorption for the studied Ag I lines at the wavelengths of 327.9 nm and 338.2 nm. The center dip is associated with self-reversal due to self-absorption in the plasma. The Q-switched radiation of 355 nm, 532 nm, or 1064 nm from a Nd:YAG laser device generates the plasma at the surface of silver nano-material targets, with experiments conducted in standard ambient temperature and pressure laboratory air. Procedures for recovery of the spectral line shapes confirm that over and above the effects of self-reversal, line shape distortion are important in the analysis. The work discusses parameters describing self-absorption when using fluence levels of 2 to 33 J/cm2 to generate the plasma. Furthermore, subsidiary calibration efforts that utilize the hydrogen alpha line of the Balmer series show that the Ag I lines at 827.35 nm and 768.7 nm are optically thin.