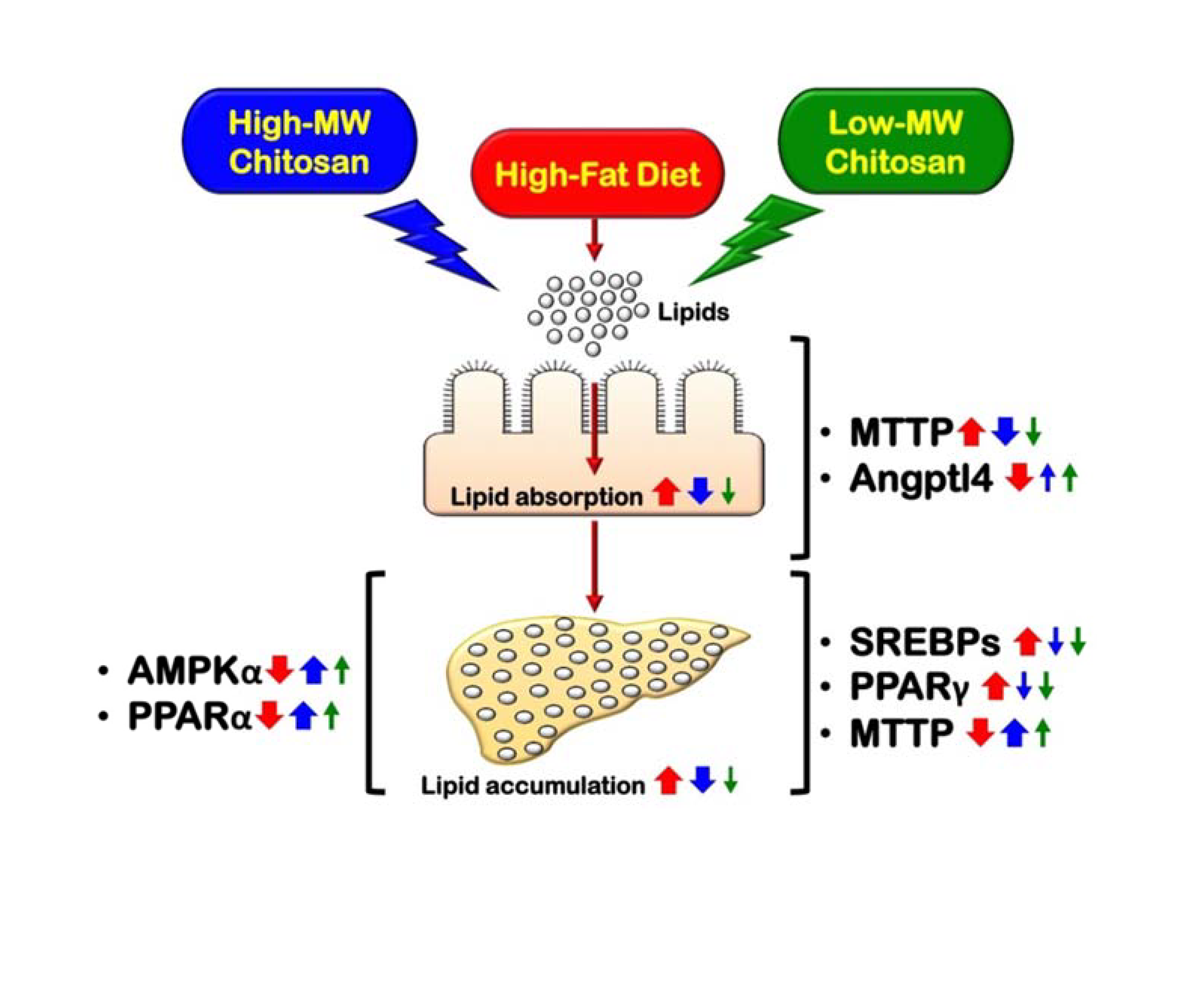
The present study examined and compared the effects of high- and low-molecular weight (MW) chitosan, a nutraceutical, on intestinal and liver lipid metabolism in rats fed with high-fat diet. Both high- and low-MW chitosan decreased liver weight, elongated small intestine, improved the dysregulation of blood lipids and liver fat accumulation, and increased fecal lipid excretion in high-fat diet-fed rats. Supplementation of both high- and low-MW chitosan significantly inhibited the decreased phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)α and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)α protein expressions and the increased lipogenesis/cholesterogenesis-associated protein expressions (sterol regulatory element binding protein (SREBP)1c, SREBP2, and PPARγ) and the decreased apolipoprotein (Apo)E and microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTTP) protein expressions in the livers of high-fat diet-fed rats. Both high and low-MW chitosan supplementation could also suppress the increased MTTP protein expression and the decreased angiopoietin-like protein (Angptl)4 protein expression in the intestines of high-fat diet-fed rats. Comparison between high and low-MW chitosan, high-MW chitosan has a higher efficiency than low-MW chitosan on the inhibition of intestinal lipid absorption and the increase of hepatic fatty acid oxidation, which can improve liver lipid biosynthesis and accumulation.