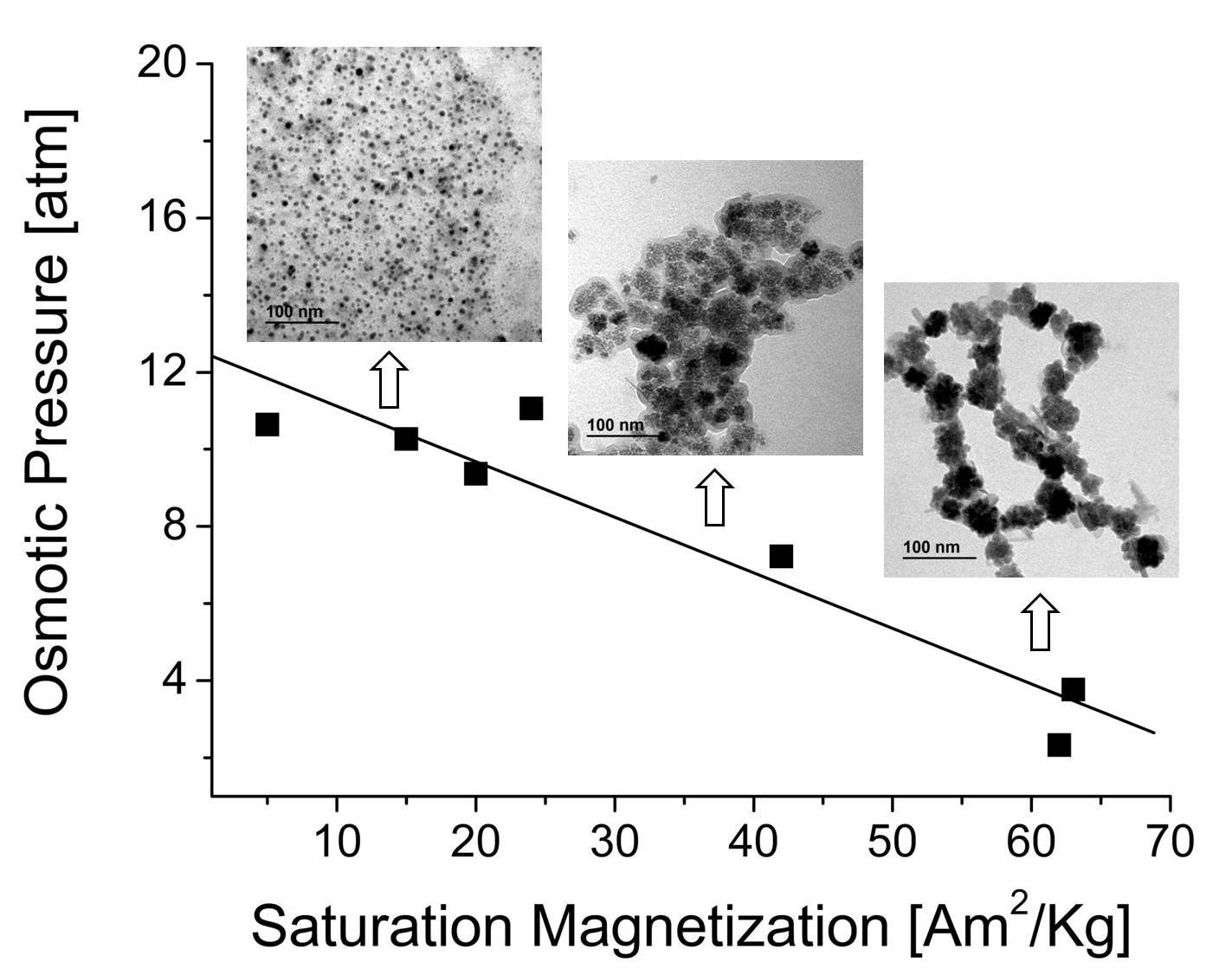
Aqueous dispersions of magnetic nanocomposites have been proposed as draw electrolytes in forward osmosis. One possible approach for the production nanocomposites based on magnetite nanoparticles and sodium polyacrylate, is the synthesis of the magnetic iron oxide by coprecipitation or oxidative precipitation in presence of an excess of the polymer. In this work we explored the effect of the polymer proportion on the nanomaterials produced by these procedures. The materials obtained were compared s with the obtained by the coating of magnetite nanocrystals produced beforehand with the same polymer. The samples were characterized by chemical analysis, photon correlation spectroscopy, thermogravimetry, X-ray diffraction, infrared spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy and magnetometry. The general trend observed is that part of the polymer is incorporated to the magnetic material during the synthesis heavily modifying its texture, with a drastic reduction of the particle size and magnetic response. The aqueous dispersions of the nanocomposites were highly stable with hydrodynamic size roughly independent on the polymer proportion. Their osmotic pressure proportional to the concentration of the polyelectrolyte, was similar than the generated by the equivalent amount of free polymer in the case of samples generated by oxidative precipitation and smaller in the case of samples generated by coprecipitation. Finally the possibilities of using these materials as draw electrolytes in forward osmosis will be briefly discussed.