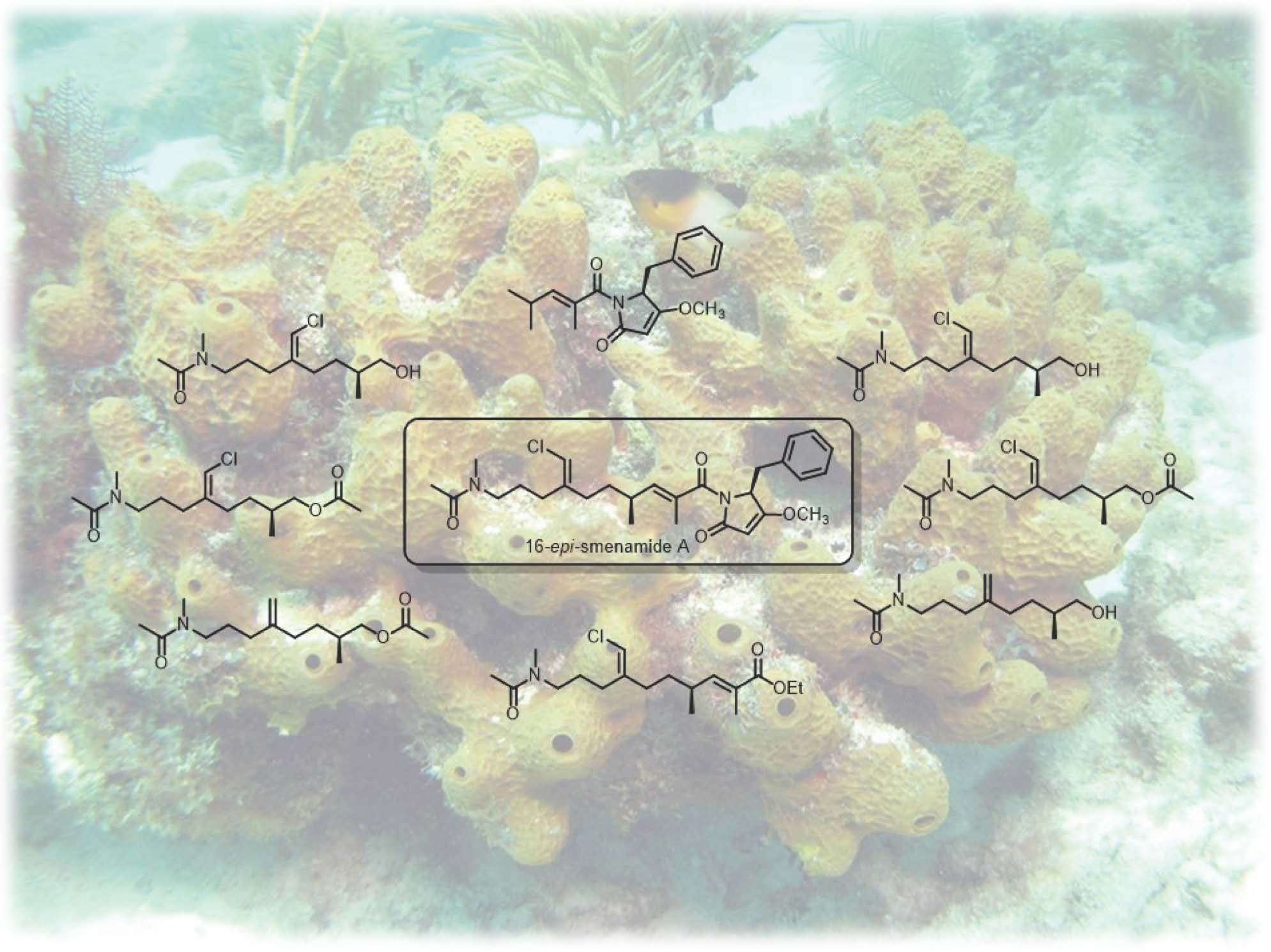
Smenamides are an intriguing class of peptide/polyketide molecules of marine origin showing antiproliferative activity against lung cancer Calu-1 cells at nanomolar concentrations through a clear pro-apoptotic mechanism. To probe the role of the activity-determining structural features, the 16-epi-analogue of smenamide A and eight simplified analogues in the 16-epi series were prepared using a flexible synthetic route. The synthetic analogues were tested on multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines showing that the configuration at C-16 slightly affects the activity, since the 16-epi-derivative is still active at nanomolar concentrations. Interestingly, it was found that the truncated compound 8, mainly composed of the pyrrolinone terminus, was not active while compound 17, essentially lacking the pyrrolinone moiety, was 1000-fold less active than the intact substance and was the most active among all the synthesized compounds.