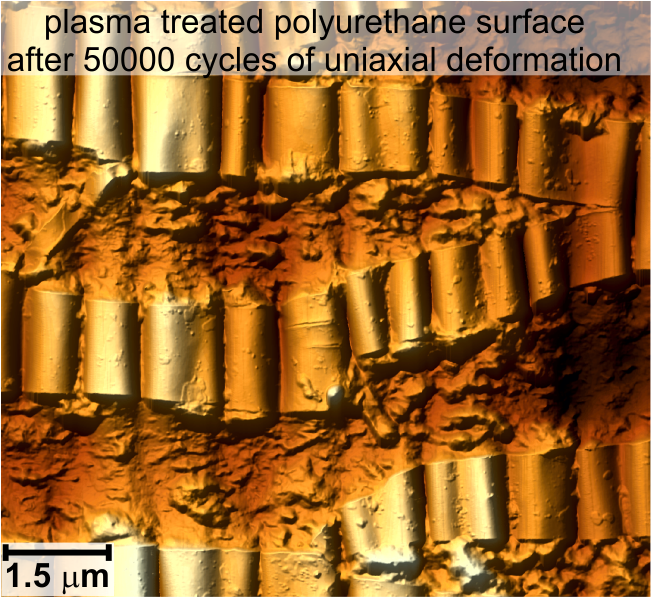
Plasma treatment of soft polymers is the promising technique to improve biomedical properties. The response to the deformation of such materials is not yet clear. Soft elastic polyurethane treated with plasma immersion ion implantation is subjected to fatigue uniaxial loading (50000 cycles, frequency – 1 Hz, strain amplitude – 10, 20, 40%). The influence of the strain amplitude and the plasma treatment regime on damage character is discussed. Surface defects are studied in unloaded and stretched states of the material. As a result of fatigue loading, transverse cracks (with closed overlapping edges as well as with open edges deeply propagating into the polymer) and longitudinal folds which are break and bend inward, appear on the surface. Hard edges of cracks cut the soft polymer which is squeezed from the bulk to the surface.