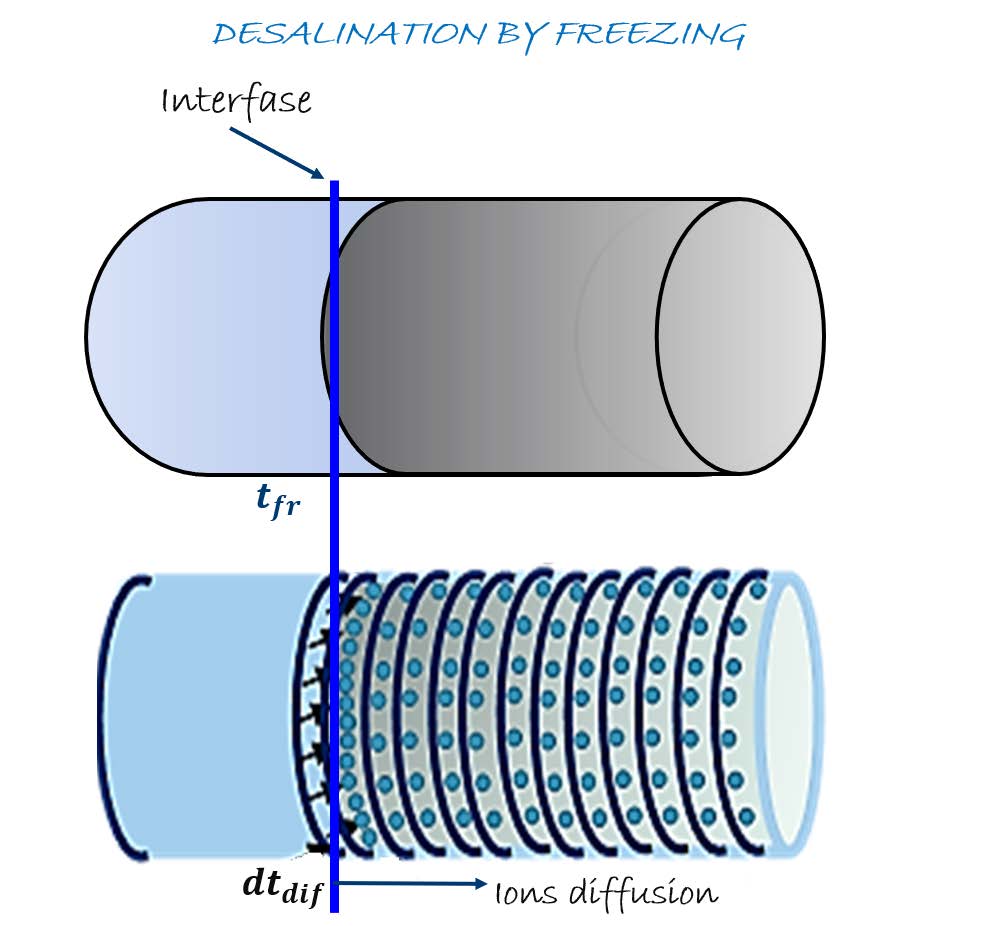
Considering the important demand of fresh water and its scarce availability, water desalination is an interesting technology, producing about 44 Mm3/year worldwide, but, in general the most common desalination techniques are highly energy demanding. Freezing-Melting (F/M) desalination uses just up to 70% less thermal energy, but is the least used process mainly, due to the difficulty of the salt separation. This study proposes a model able to analyses the thermodynamic potential that allows the salt diffusion during the F/M process, using an aqueous solution of sodium chloride. This should allow to obtain a sensitive analysis of the process to promote the separation between the high concentration brine and the ice with liquid separation by physical process. The unidimensional model is based on the evolution of both processes: thermal and mass diffusions, depending on temperature and saline gradients, predicting whether the salt will remain inside the ice or not. Thus, the thermal potential is adjusted to frozen only when the salt has been "pushed" towards the brine. Mostly models have base their results on the assumption of a “certain value of saline concentration of the liquid fraction”, value in which there is great disagreement. In this paper the calculations are based on the concentration in the solid-liquid interface, which has been extensively studied and there is a coincidence in those results, being the main advantage of the proposed model.