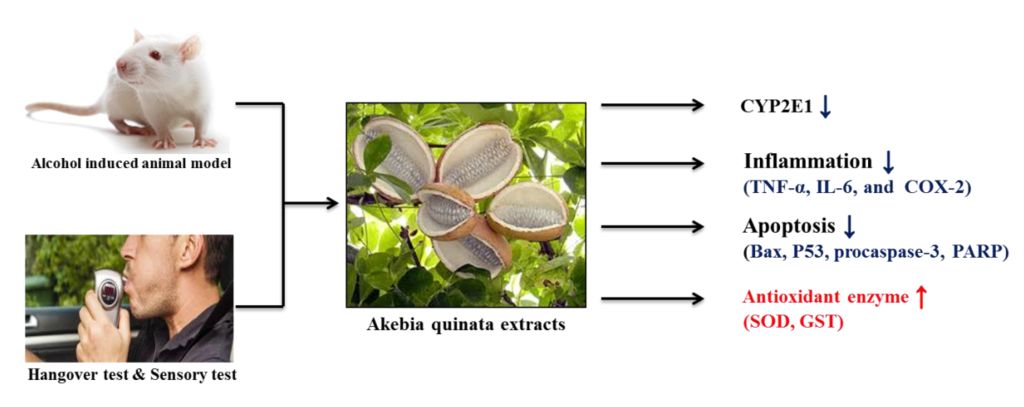
In this study, we investigated the effects of Akebia quinata ethanol extract (AE), Akebia quinata sikhye (AS), and Akebia quinata water extract (AW) on alcohol-induced liver injury in rats. The hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and antioxidant effects of AE, AS, and AW were examined. Experimental animals were randomly divided into five groups: normal, ethanol, AE (10 mL/kg), AS (10 mL/kg), and AW (10 mL/kg). Each group was administered the respective treatment orally once per day for 21 days. CYP2E1 mRNA expression was significantly lower in the AE, AS, and AW groups than that in the ethanol group. Pro-inflammatory cytokines including cyclooxygenase-2, IL-6, and TNF-α increased significantly in the ethanol group but these increases were ameliorated with AE, AS, and AW treatment. Moreover, the expression of the apoptosis-associated proteins Bax, p53, procaspase-3, and PARP decreased after treatment with AE, AS, and AW. The expression of antioxidant enzymes including BCL-2, SOD, and GST slightly decreased in the ethanol group, but AE, AS, and AW treatment augmented their activities. AQ extracts and AS attenuated ethanol-induced increases in the levels of phosphorylated p-AKT, p-ERK, and p-JNK. These results demonstrate that AQ is a competence indicator for inhibiting alcoholic liver injury.