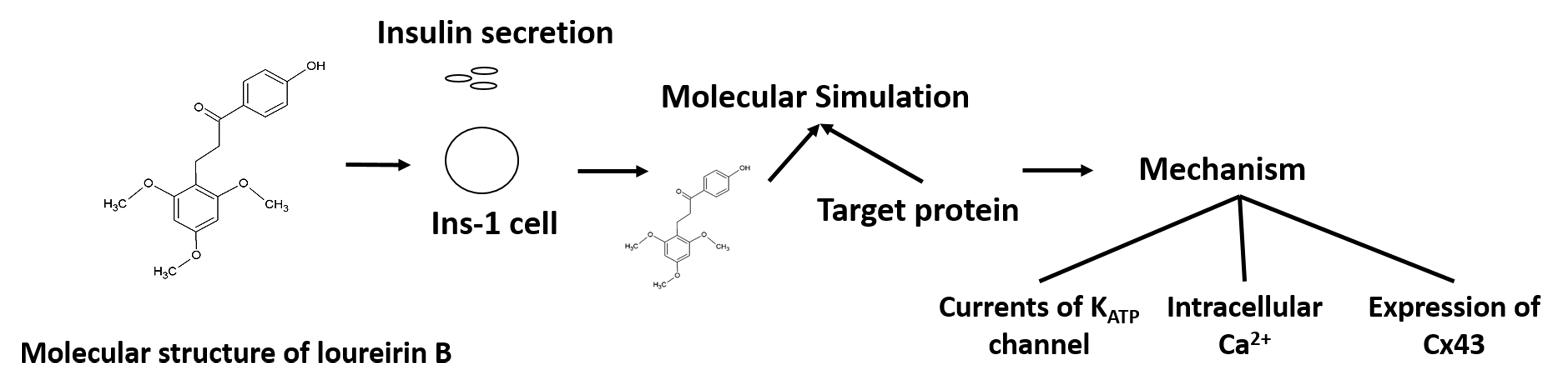
The development of new diabetes drugs continues to be explored. Loureirin B, a flavonoid, extracted from Dracaena cochinchinensis, has been confirmed to increase insulin secretion and decrease blood glucose levels. For understanding the mechanism, a series of experiments had been employed based on computational methods and cell experiments. The insulin secretion significantly increased with the incubation of 0.01μM loureirin B for 4 hours. The viability of Ins-1 cells showed no significant difference with the treatment of loureirin B. Through computational methods, we hypothesized that loureirin B could interacts with KATP channels to promote insulin secretion. In cell experiments, it could be found that the current of KATP channel of Ins-1 cells was inhibited by the effect of loureirin B. After then, the voltage-dependent calcium channels were activated, the increase of Cx43 protein expression might mediate the Ca2+ to the intracellular. In summary, it could be concluded that loureirin B promoted insulin secretion mainly through inhibiting KATP current, the influx of Ca2+ to the Intracellular and the expression of Cx43.