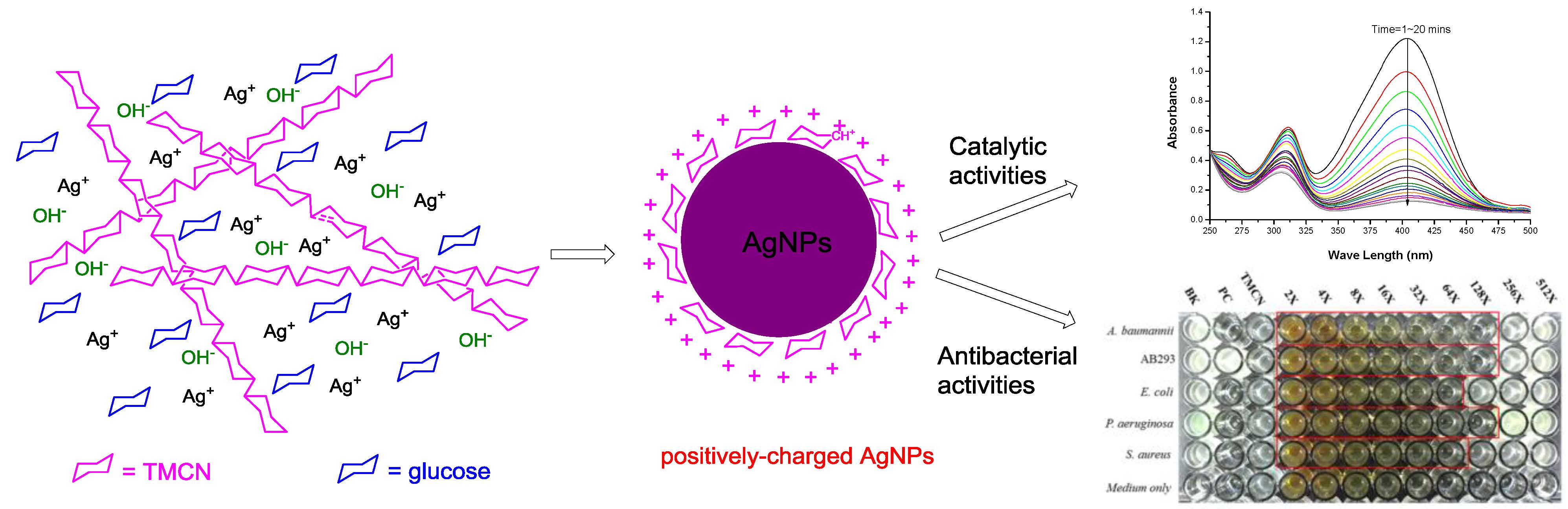
We report a facile route for the green synthesis of trimethylchitosan nitrate-capped silver nanoparticles (TMCN-AgNPs) with positive surface charge. In this synthesis, silver nitrate, glucose, and trimethyl chitosan nitrate (TMCN) were used as silver precursor, reducing agent, and stabilizer, respectively. The reaction was carried out in a stirred basic aqueous medium at room temperature without the use of energy-consuming or expensive equipment. We investigated the effects of the concentrations of NaOH, glucose, and TMCN on the particle size, zeta potential, and formation yield. The AgNPs were characterized by UV-visible spectroscopy, photon correlation spectroscopy, laser Doppler anemometry, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The catalytic activity of the TMCN-AgNPs was studied by the reduction of 4-nitrophenol using NaBH4 as a reducing agent. We evaluated the antibacterial effects of the TMCN-AgNPs on Acinetobacter baumannii, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Staphylococcus aureus using the broth microdilution method. The results showed that both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria were killed by the TMCN-AgNPs at very low concentration (< 6.13 μg/mL). Moreover, the TMCN-AgNPs also showed high antibacterial activity against clinically isolated multidrug-resistant A. baumannii strains, and the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was ≤ 12.25 μg/mL.